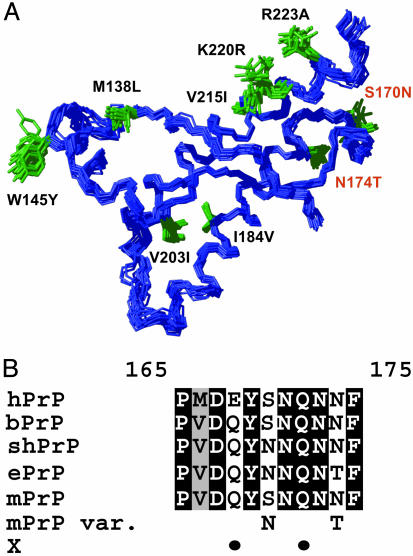
Fig. 1.
Prion protein amino acid sequence and 3D structure of the elk and other mammalian species. (A) NMR structure of ePrP(121–231) presented as a bundle of 20 energy-minimized conformers. The backbone is blue, and the amino acid side chains that are different from mPrP are shown in green and identified with black or red lettering, starting with the amino acid one-letter code for the corresponding amino acid in mPrP and followed by the sequence position and the amino acid in ePrP. The 20 conformers were superimposed for best fit of the backbone heavy atoms of residues 125–225. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of the loop region 165–175, which connects the regular secondary structures β2 and α2, for the following species: hPrP, bPrP, shPrP, ePrP, mPrP, and “mPrP var.” (mPrP with designed amino acid replacements in positions 170 and 174). “X” indicates with black dots the positions 168 and 172 that have been proposed to be part of an epitope for interactions with a species-specific protein X (23). Identical amino acids in the five proteins are shown on a black background, conservative substitutions are shown on gray, and nonconservative replacements are on a white background.