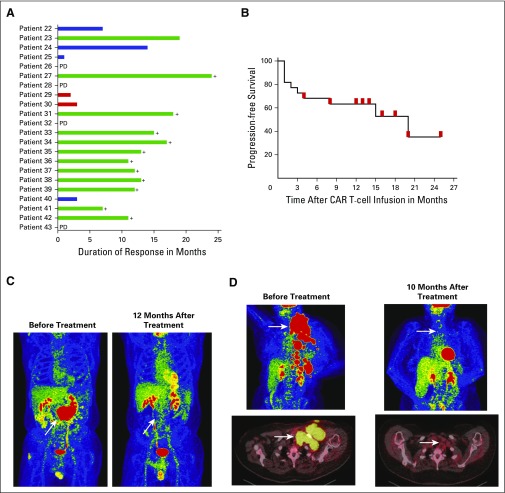
Fig 2.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting CD19 (CAR-19) T cells eradicated large masses of chemotherapy-refractory lymphoma. (A) Graphical representation of the types of antilymphoma responses and the durations of responses. (B) Progression-free survival starting at the day of cell infusion and ending at the day of disease progression is shown for all patients. Red marks indicate censored patients with ongoing complete remissions (CRs) at the time of last follow-up with one exception: the red mark at 4 months after CAR T-cell infusion indicates the time point when patient 40 underwent allogeneic stem-cell transplantation while in partial remission. Two patients were censored at the 13-month time point and three patients were censored at the 14-month time point, but there is only one red mark on the graph for each of these time points. (C) Patient 35 had received four types of lymphoma therapy, and his diffuse large B-cell lymphoma was chemotherapy refractory at the time of protocol enrollment. After CAR-19 T-cell infusion, his lymphoma entered an ongoing CR. (D) At the time of protocol enrollment, patient 38 had received five types of prior lymphoma therapy, and her diffuse large B-cell lymphoma was refractory to chemotherapy. After CAR-19 T-cell infusion, the lymphoma entered an ongoing CR. For (C) and (D), the white arrows indicate sites of lymphoma. Residual red-colored areas in the after-treatment images are normal findings in the brain, heart, kidneys, and bladder. PD, progressive disease.