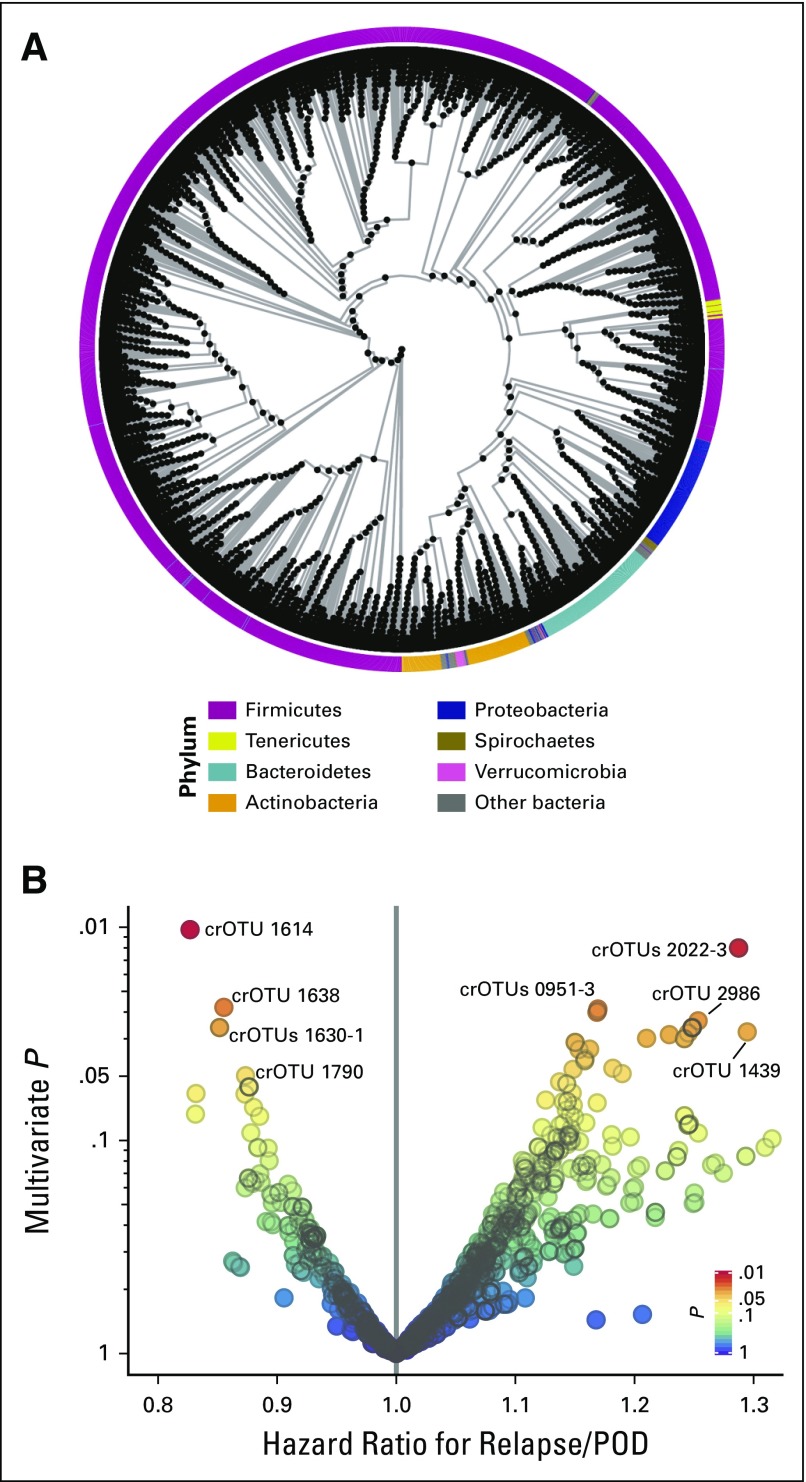
Fig 1.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of operational taxonomic units (OTUs) and clusters of related OTUs (crOTUs). Each black point is a crOTU. Phylum is color coded along the circumference. A schematic of how the tree was constructed and a detailed tree are presented in the Data Supplement. (B) Volcano plot of multivariable P values of crOTUs against the multivariable hazard ratios for relapse/progression of disease (POD) in the discovery set. crOTUs are color coded by P value. Multivariable adjustment was performed for refined disease risk index, graft source, and conditioning intensity. The most abundant species in each of the labeled crOTUs are as follows: Eubacterium limosum in crOTU 1614; Streptococcus sinensis in crOTU 2022-3; E. limosum in crOTU 1638; E. limosum in crOTU 1630-1; Parvimonas micra in crOTU 1790; Leptotrichia hongkongensis in crOTU 0951-3; Flavonifractor plautii in crOTU 2986; and Actinomyces odontolyticus in crOTU 1439. OTU-level analysis and univariable analysis results are presented in the Data Supplement. crOTU composition at the species level and numeric values are tabulated for the top candidates and for all candidates in the Data Supplement.