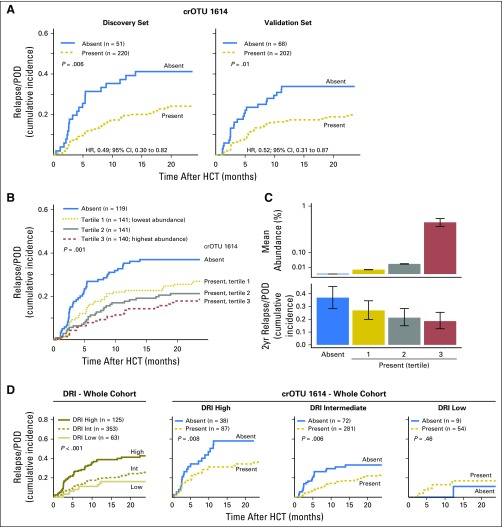
Fig 2.
Cluster of related operational taxonomic units (crOTU) 1614, which includes members of the family Eubacteriaceae, is associated with decreased relapse/progression of disease (POD) after allogenic hematopoietic-cell transplantation (allo-HCT). (A) Cumulative incidence of relapse/POD in the discovery (n = 271) and validation (n = 270) sets stratified by presence or absence of crOTU 1614. (B) Cumulative incidence of relapse/POD in the whole cohort (N = 541) stratified by crOTU 1614 abundance. (C) Upper panel, mean abundance of crOTU 1614 in the four strata (error bars are standard error of the mean) and, lower panel, cumulative incidence of relapse/POD at 2 years in the four strata (error bars are 95% CIs). (D) Far left: refined disease risk index (DRI) alone stratifies the relapse/POD risk in this cohort. Three right panels: crOTU 1614 presence further stratifies relapse among patients with high-risk and intermediate-risk DRIs. Patients with very-high-risk DRIs were grouped together with those who had high-risk DRIs. HR, hazard ratio.