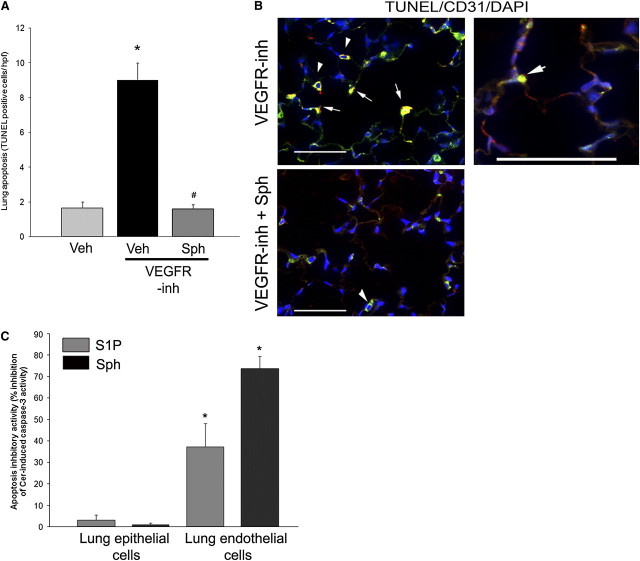
Figure 4.
Antiapoptotic effects of d-sphingosine. (A) Lung apoptosis (number of terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase–mediated dUTP nick end labeling [TUNEL]-positive cells per high-power lung field [hpf] measured on coded slides) was increased in response to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor (VEGFR-inh), but not in mice supplemented with d-sphingosine (Sph) (mean + SEM; *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle [Veh]; #P < 0.05 vs. VEGFR-inh; Student's t test; n = 3–6). (B) Coimmunolocalization of TUNEL-positive apoptotic cells (green) with endothelial cell marker (CD31, red) in lungs treated with VEGFR-inh with or without Sph supplementation. Note TUNEL-positive nuclear staining of CD-31 decorated cells (arrows). Alveolar macrophages exhibited typical green autofluorescence (arrowheads). Scale bars, 50 μm. (C) Inhibitory activity of sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P, 1 μM) or Sph (1 μM) cotreatments on ceramide-induced caspase-3 activity measured by kinetic fluorimetry (U/min) normalized by protein concentration in lysates of primary rat lung epithelial and endothelial cells. The inhibitory activity was calculated relative to the apoptotic activity induced by ceramide 16:0 (Cer, 10 μM, 24 h) treatment in the absence of S1P or Sph (mean + SEM; *P < 0.05 vs. inhibitory activity of the respective S1P agonist on epithelial cells; n = 3). DAPI = 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.