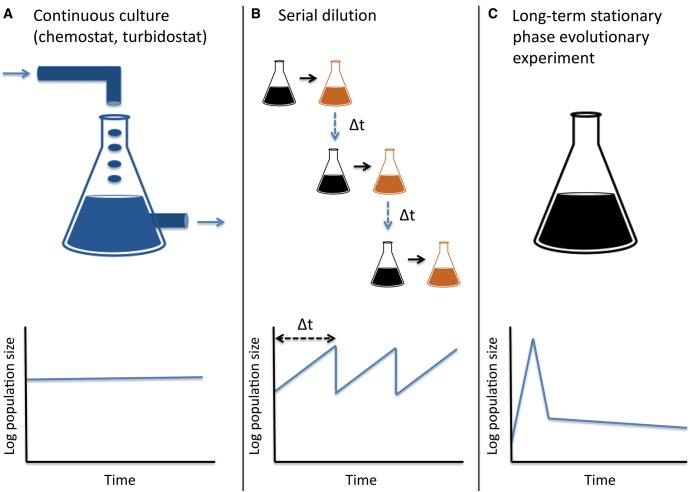
Fig. 1.
Experimental evolutionary setups. (A) Continuous culture—Through a constant inflow of nutrients and outflow of random cells and waste, bacteria are allowed to grow continuously, while maintaining a nearly constant population size (B) Serial dilution—semi-continuous growth—bacteria are transferred into fresh media at set intervals, allowing for a consistent number of replications between dilution cycles. (C) LTSP evolutionary experiments—bacteria are only initially provided with resources needed for growth. Shortly after they spend their resources they enter a phase of accelerated death, followed by LTSP. Panels A and B of this figure were adapted from (Barrick and Lenski, 2013).