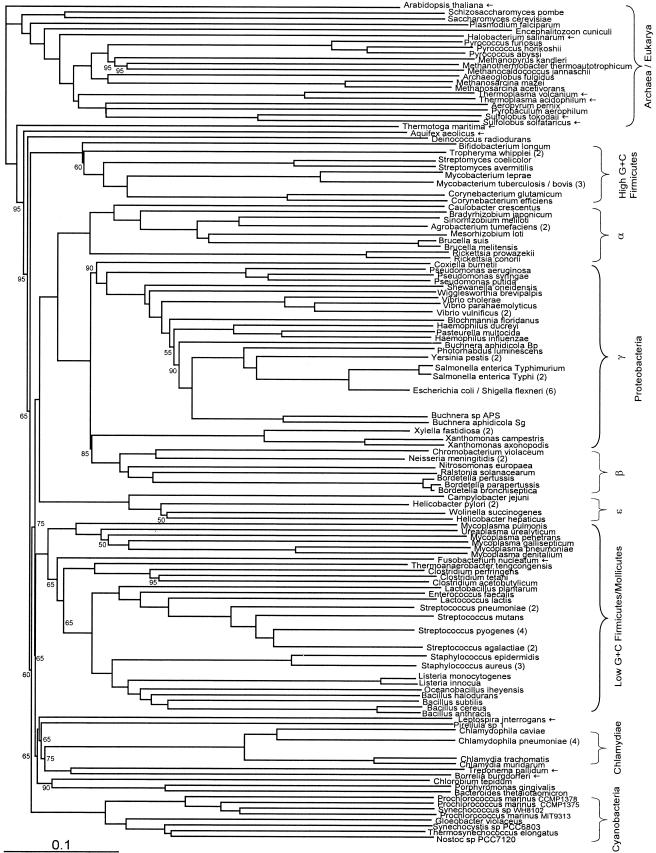
FIG.1.
Fitch-Margoliash tree based on conceptually translated complete genomic ORF sets, with equal weighting of all genes shared between a pair of genomes (see text for details). Bootstrap support (percentage of 20 replicates) was determined in a separate analysis by strict consensus. Where support is not shown, it is 100%. Where a node is marked with an empty circle, support is less than 50%. Taxa of particular interest are marked with an arrow. Whenever different strains of a single species form a single clade, they have been united to a single branch and the number of strains is given in parentheses as follows: Tropheryma whipplei includes T. whipplei Twist and TW0827; Mycobacterium tuberculosis/bovis includes M. bovis, M. tuberculosis H37Rv, and M. tuberculosis CDC1551; Agrobacterium tumefaciens includes A. tumefaciens C58 from both the Cereon and Dupont genomes; Vibrio vulnificus includes V. vulnificus strains CMCP6 and YJ016; Salmonella enterica Typhi includes S. enterica serovar Typhi strains CT18 and Ty2; Escherichia coli/Shigella flexneri includes E. coli strains O157:H7 EDL933, O157:H7, CFT073, and K-12 and S. flexneri strains 2a 2457T and 2a 301; Xylella fastidiosa includes X. fastidiosa strains 9a5c and Temecula1; Neisseria meningitidis includes strains MC58 and Z2491; Helicobacter pylori includes strains 26695 and J99; Streptococcus pneumoniae includes strains R6 and TIGR4; Streptococcus pyogenes includes strains MGAS315, SSI1, SF370, and MGAS8232; Streptococcus agalactiae includes strains 2603VR and NEM316; Staphylococcus aureus includes strains N315, Mu50, and MW2; and Chlamydophila pneumoniae includes strains AR39, TW183, J138, and CWL029. Branch end points for these species correspond to the former root of the clade of strains. For the full trees, which include all strains, see the supplemental material.