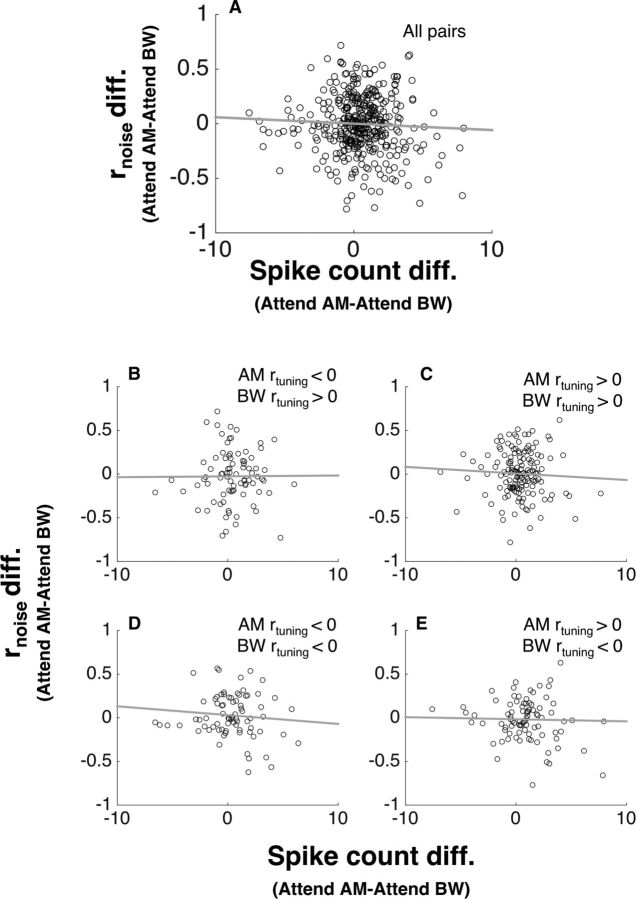
Figure 7.
Attention-related effects on rnoise are independent of attention-related changes in spike count. A, For each pair in our sample, we plotted the spike count difference against the rnoise difference (attend AM − attend BW). We found no significant relationship between the effect of attention on spike count and the effect of attention on rnoise (p > 0.05). B–E, Same analysis as in A, but for pairs from each of the four rtuning categories. For none of these groups did we find any significant relationship between attention-related rnoise effects and attention-related spike count effects.