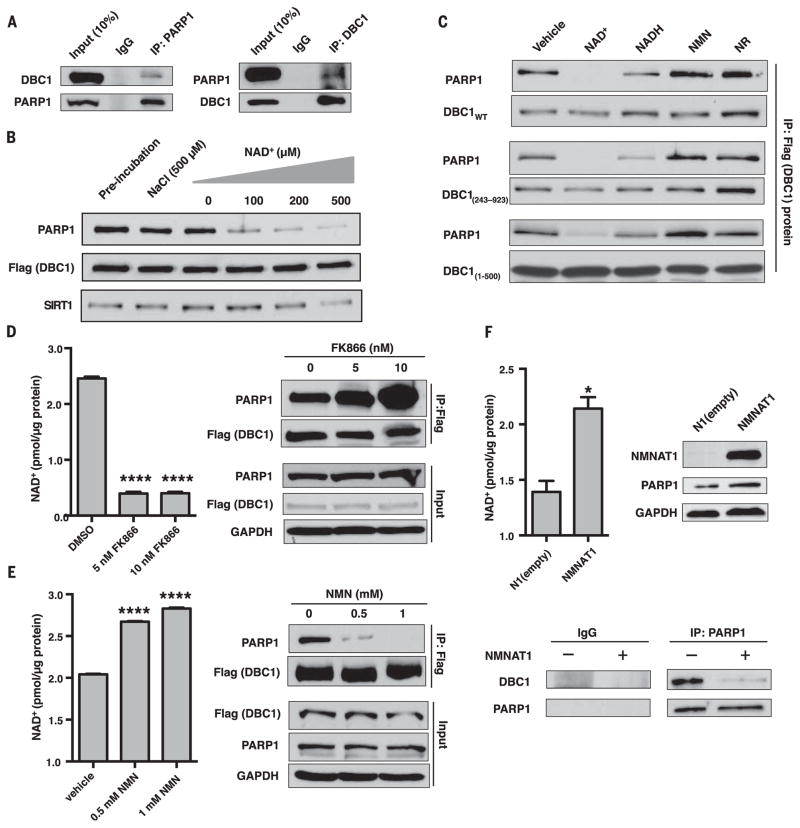
Fig. 1. Regulation of the PARP1-DBC1 interaction by NAD+.
(A) Endogenous DBC1 and PARP1 interact. IgG, immunoglobulin G; IP, immunoprecipitation. (B) NAD+ dissociates the PARP1-DBC1 interaction. (C) Effects of NAD+ and structurally related molecules on the PARP1-DBC1 interaction. Flag-DBC1 was incubated with molecules (200 μM) for 1 hour and then probed for PARP1. NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; NR, nicotinamide riboside; WT, wild type. (D to F) The PARP1-DBC1 interaction after treatment with (D) FK866 or (E) NMN for 24 hours or (F) in cells overexpressing NMNAT1, an NAD+ salvage pathway gene to raise NAD+. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. (D and E) One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Sidak’s post-hoc correction. (F) Unpaired two-tailed t test. *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001.