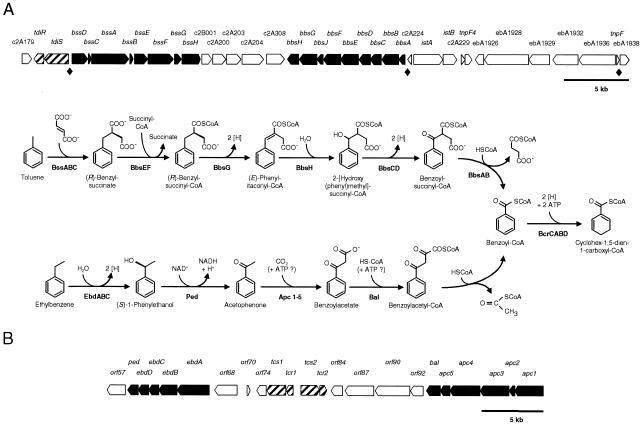
FIG. 1.
Anaerobic toluene and ethylbenzene degradation in strain EbN1 proceed via different reaction sequences to the first common intermediate, benzoyl-CoA. (A) Pathway of anaerobic toluene degradation (modified from references 4 and 33). Enzyme names of indicated gene products (shown in boldface type) (31) are as follows: BssABC, benzylsuccinate synthase; BbsEF, succinyl-CoA:(R)-benzylsuccinate CoA-transferase; BbsG, (R)-benzylsuccinyl-CoA dehydrogenase; BbsH, phenylitaconyl-CoA hydratase; BbsCD, 2-[hydroxy(phenyl)methyl]-succinyl-CoA dehydrogenase; BbsAB, benzoylsuccinyl-CoA thiolase. (B) Pathway of anaerobic ethylbenzene degradation (modified from references 2, 28, 38, and 39). Enzyme names of indicated gene products (shown in boldface type) (42) are as follows: EbdABC, ethylbenzene dehydrogenase; Ped, (S)-1-phenylethanol dehydrogenase; Apc1-5, acetophenone carboxylase; Bal, benzoylacetate CoA-ligase. Anaerobic degradation of benzoyl-CoA is initiated by benzoyl-CoA reductase (BcrCABD) and then further oxidized via reductive ring cleavage to carbon dioxide (not shown; 4). Reducing equivalents ([H]) are used for the reduction of nitrate to dinitrogen. A scale model for the organization of the involved genes is displayed for both pathways. Annotations for ebA1926 through ebA1938 genes are provided in Table 4, while those for all other genes have already been described elsewhere (31, 42). ♦, consensus sequence TTA(A/G)GTGTTCGCACCAATTG in the promoter regions of bssD, bbsA, and the ebA1936 gene is located 118, 68, and 450 bp upstream of the respective translational starts.