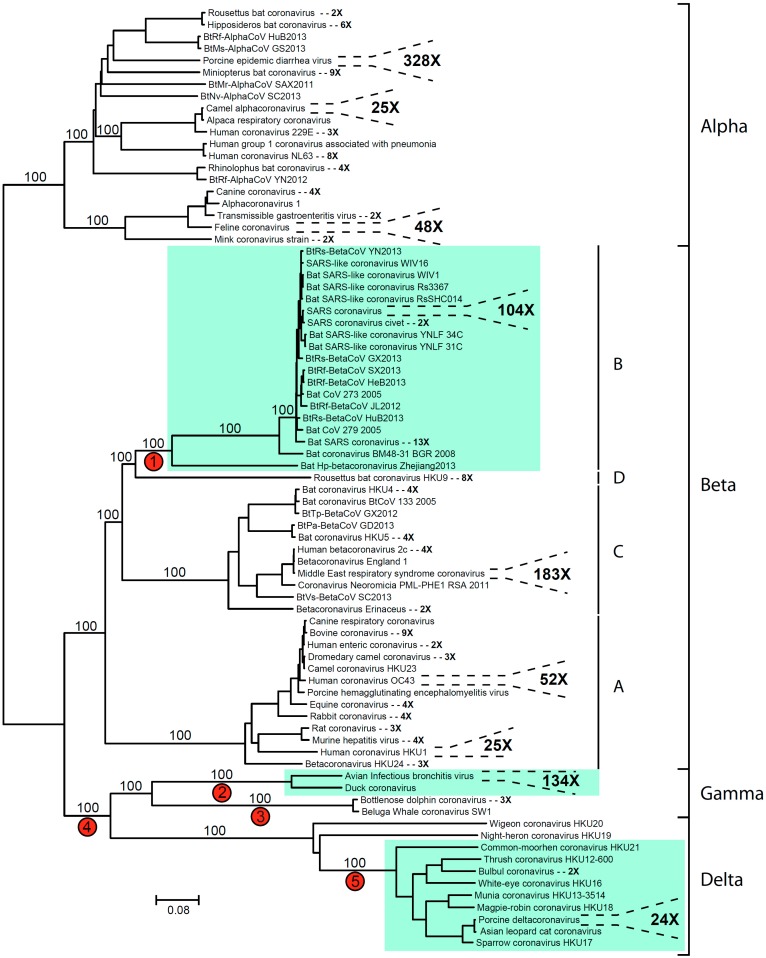
Figure 1.
Coronavirus phylogeny with s2m-containing sequences highlighted. ORF1ab polyprotein amino acid sequences were aligned using the program MUSCLE [8] and default parameters. The phylogenetic analysis was performed using the program SeaView [9] and the neighbor joining clustering method with Kimura two-parameter distances. In order to avoid large clades of closely related sequences, operational taxonomic units (OTUs) with similar GenBank taxonomical annotation and almost identical sequences were identified and basal members of these monophyletic groups chosen to represent such sequence clusters. For instance, there are 183 complete ORF1ab polyprotein sequences available from different strains of the Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) coronavirus. These sequences are represented by a single accession (in this case, GenBank accession number ALB08298; isolate KOREA/Seoul/035-1-2015). Based on visual inspection of the alignment it was determined that the sequences belonging to the Torovirinae subfamily could not be reliably aligned and were excluded from the analysis. Brackets show serogroups as well as betacoronavirus lineages and key branches with 100% bootstrap support (100 pseudoreplicates) have been indicated. Red circles indicate possible losses/gains of s2m (see discussion in text).