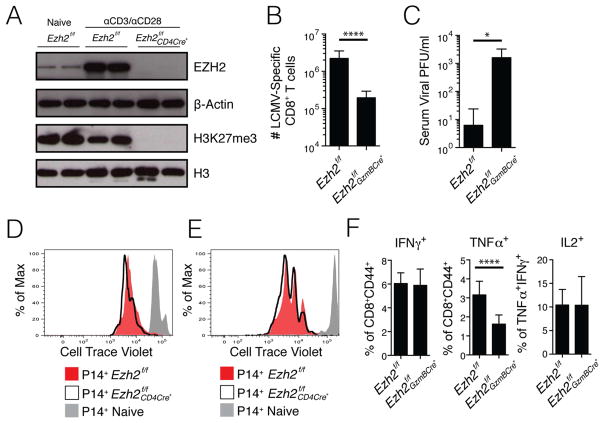
Figure 3. EZH2 is required for H3K27me3 deposition and antiviral CD8+ T cell clonal expansion.
A) Naïve CD8+ T cells from Ezh2f/f mice and CD8+ T cells from Ezh2f/f and Ezh2f/f CD4Cre+ mice activated in vitro with αCD3 and αCD28 for 3 day were purified using FACS and the amounts of EZH2, β-Actin, H3K27me3 and total H3 were measured by western blot (data from 2 different experiments). Note, H3K27me3 is virtually undetectable in activated Ezh2f/f CD4Cre+ CD8+ T cells.
B) Ezh2f/f and Ezh2f/f GzmBCre+ mice were infected with LCMV Armstrong and the number of splenic DbGP33-41 and DbNP396-404 MHC class I tetramer+ CD8+ T cells combined were enumerated at d8 p.i.
C) Bar graph shows viral titer in the serum of Ezh2f/f and Ezh2f/f GzmBCre+ mice at d8 p.i.
D) Naïve P14 Ezh2f/f (red) and Ezh2f/f CD4Cre+ (black line) CD8+ T cells were labeled with CellTrace Violet and stimulated for 72 hours in vitro with GP33-41 peptide. Unstimulated naïve P14 CD8 T cells are shown in gray.
E) Congenically mismatched naïve P14+ Thy1.1+Ly5.2+ Ezh2f/f (red) and Thy1.2+Ly5.2+ Ezh2f/f CD4Cre+ (black line) CD8+ T Cells were pulsed with CellTrace Violet and adoptively co-transferred into Thy1.2+ Ly5.1+ WT recipient mice that were subsequently infected with LCMV-Armstrong and analyzed for cell division 60 hours later. P14+ CD8+ T cells from an uninfected recipient are shown in gray.
F) Bar graphs show IFNγ, TNFα, and IL2 production in GP33-41 peptide-stimulated Ezh2f/f and Ezh2f/f GzmBCre+ CD8+ T cells at d8 p.i.
Data shown are representative of two (C–E), three (A), or five (F) independent experiments (n=4–10 mice/group/experiment for C and F), or cumulative of five independent experiments (n=21 mice/group) (B). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *p=0.02, ****p<0.0001