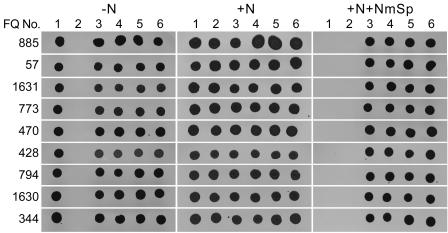
FIG. 3.
Tests of complementation by clones bearing, intact, only the gene mutated in the corresponding mutant: FQ885 (alr2825) plus pRL2875, FQ57 (alr2827) plus pRL2864, FQ1631 (alr2831) plus pRL2862, FQ773 (alr2832) plus pRL2863, FQ470 (alr2833) plus pRL2865a, FQ428 (alr2837) plus pRL2877, FQ794 (alr2839) plus pRL2876, FQ1630 (alr2840) plus pRL2873, and FQ344 (alr2841) plus pRL2866. Spots were grown from cells of wild-type Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 (lanes 1), a particular FQ mutant (lanes 2), and four independent, exconjugant clones of the particular FQ mutant bearing the corresponding pRL plasmid (lanes 3 to 6). The left, center, and right panels present, respectively, the results observed (for any one mutant, simultaneously) 2 to 3 weeks after spotting cells on agar-solidified media AA, AA+N, and AA+N plus 200 μg of Nm ml−1 and 10 μg of Sp ml−1. Cells of the wild-type strain grew in the presence or absence of nitrate but failed to grow in the presence of antibiotic; cells of each mutant grew in the presence of nitrate unless counterselected by antibiotics, but failed to grow in the absence of nitrate; addition of the corresponding cloned genes permitted the mutants to grow with only N2 as nitrogen source or in the presence of antibiotics.