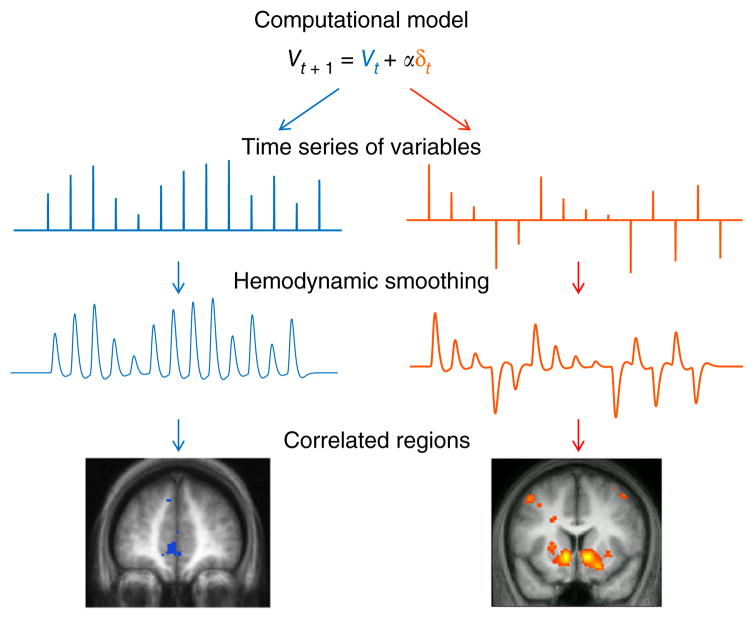
Figure 3.
Schematic of model-based fMRI. A computational model (top; error-driven reward-learning model) can be used to generate candidate time series of internal variables (values, V, in blue and prediction errors, δ, in red). Following smoothing to account for the hemodynamic lag (middle), these variables can be used as regressors to seek correlated BOLD activity in the brain (bottom), producing regions that can be considered candidates for performing or tracking the corresponding computations in the model. α, learning rate parameter.