FIGURE 3. Voluntary exercise prevents CFA-induced reductions in heart rate variability.
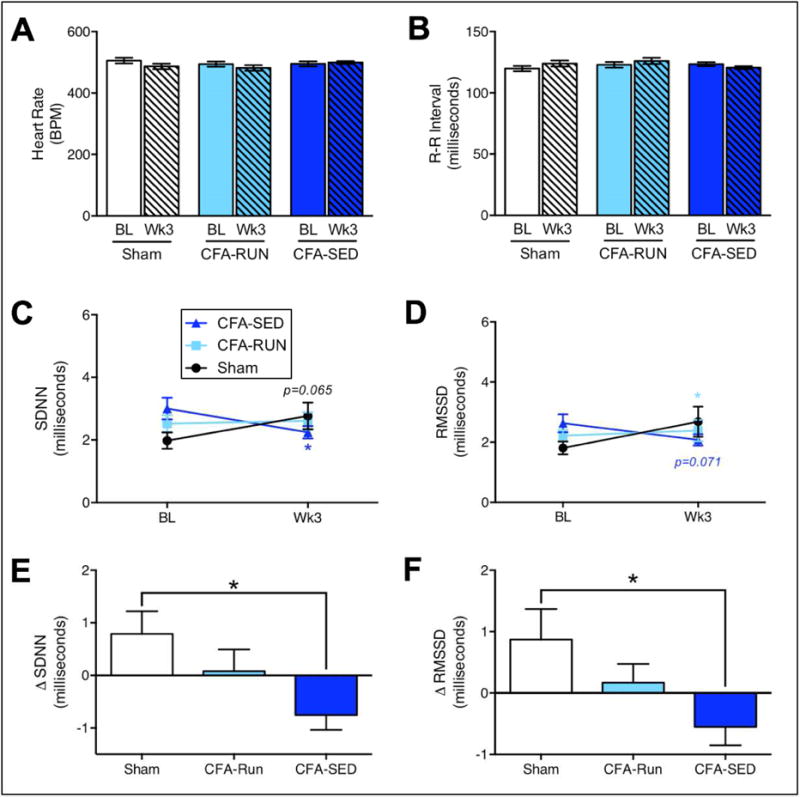
(A/B) Neither heart rate nor R-R interval were significantly changed by CFA or access to running wheels. (C) However, a significant decrease in SDNN for the CFA-SED group along with a trend toward increased SDNN for the sham group were found. (D) Similarly, a trend toward a decrease in RMSSD for the CFA-SED group along with a significant increase in SDNN for the sham group were found. Delta scores for SDNN and RMSSD showed that CFA-induced decreases in both SDNN (E) and RMSSD (F) were mitigated in the CFA-RUN group. Stars (*) signify significant comparisons with sham group. */p<0.05, n=16–34.
