Fig. 8.
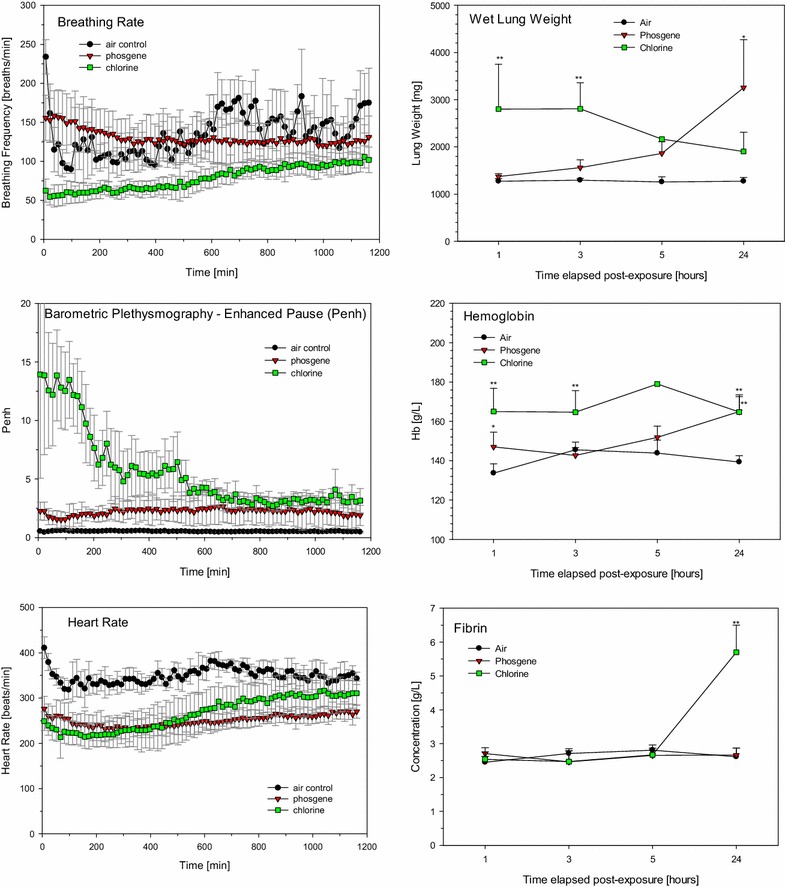
Comparison of three groups of rats sequentially nose-only exposed for 30 min to air, ≈32 mg/m3 (≈8 ppm) phosgene gas, or 197 mg/m3 (413 ppm) chlorine gas. Cardiopulmonary endpoints were determined as detailed in the caption of Fig. 2. Lung weights, hemoglobin, and fibrin were determined 1, 3, 5, and 24 h post-phosgene exposure (for details see [47]). Data points represent means ± SD (n = 6; however, due to unscheduled deaths in the chlorine group the actually examined number of rats were 3, 1, and 4 at the 3, 5, and 24 h sacrifices, respectively. Asterisks (*) denote significant differences between the phosgene and chlorine groups (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01)
