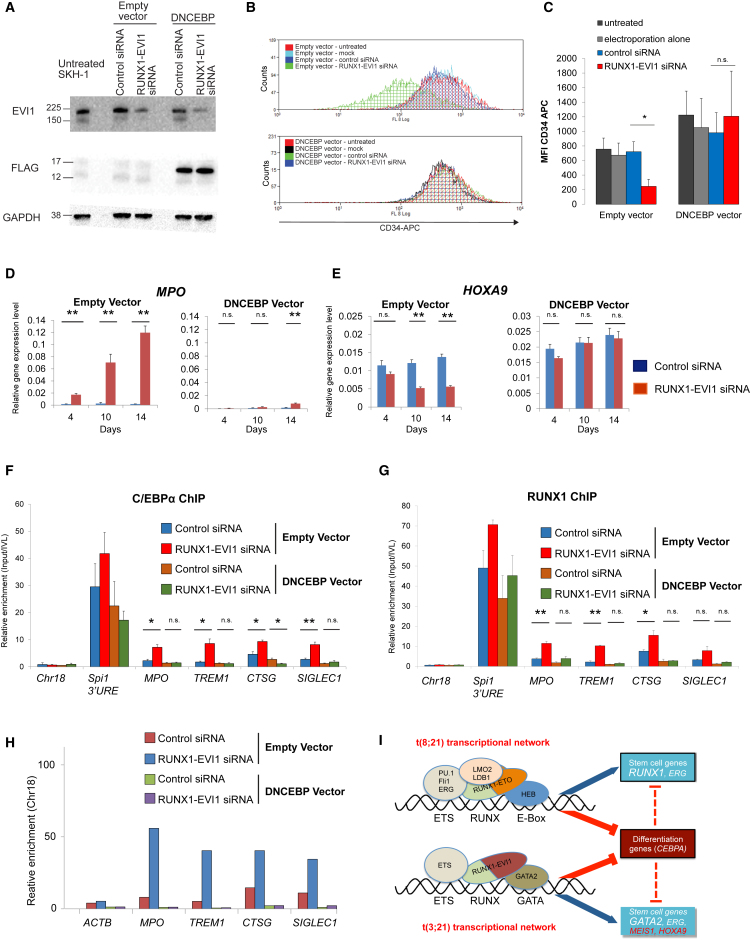
Figure 7.
C/EBPα DNA Binding Ability Is Critical for the Effects of RUNX1-EVI1 Knockdown
(A) Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates of untreated t(3;21) SKH-1 cells and empty or DNCEBP vector transduced SKH-1 cells, transfected with either control or RUNX1-EVI1 siRNA after 14 days. Sizes (in kDa) are indicated. The blot was probed with EVI1, FLAG, or GAPDH antibodies (loading control) as indicated.
(B and C) Flow cytometry of empty and DNCEBP vector transduced SKH-1 cells, untreated or after 14 days of mock, control, or RUNX1-EVI1 siRNA treatment, stained with CD34-APC. (B) Representative histogram with overlay of different treatment conditions. (C) Graph of median fluorescence intensity (MFI) (median) of CD34-APC staining. Bars represent different treatment conditions. Mean of three independent experiments is shown, and error bars represent SEM. n.s., not significant; ∗p < 0.05 (paired t test).
(D and E) RT-PCR analysis of mRNA levels of the indicated genes with and without RUNX1-EVI1 knockdown in the presence and absence of DNCEBP. (D) MPO. (E) HOXA9. mRNA levels relative to GAPDH in either empty vector or DNCEBP vector transduced SKH-1 after either control or RUNX1-EVI1 siRNA transfection (4, 10, or 14 days of treatment). The graph shows mean and SEM of three independent experiments. n.s., not significant; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01 (unpaired t test).
(F and G) ChIP-qPCR with chromatin from empty or DNCEBP vector transduced SKH-1 10 days after either control or RUNX1-EVI1 siRNA transfection, using amplicons corresponding to the MPO and SIGLEC1 enhancers, TREM1 and CTSG promoters, the SPI1 3′ upstream regulatory element (URE) enhancer as a positive control, and chromosome 18 as a negative control. (F) C/EBPα ChIP. (G) RUNX1 ChIP. Enrichment was calculated relative to input and IVL. Mean of three independent experiments is shown, and error bars represent SEM. n.s., not significant; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01 (unpaired t test).
(H) DNase I accessibility measurement using qPCR validation at MPO and SIGLEC1 enhancer and TREM1 and CTSG promoter. DNase I digestion was performed on empty vector and DNCEBP vector transduced SKH-1 following either control or RUNX1-EVI1 siRNA transfection. The ACTB amplicon was used as negative control. Enrichment was calculated relative to chromosome 18, which is a gene-free region that is DNase I inaccessible and used for normalization. A second independent experiment is shown in Figure S7D.
(I) Model depicting the binding sites and transcription factors interacting with RUNX1-ETO and RUNX1-EVI1, respectively, and their independent transcriptional networks that maintain the expression of stem cell/precursor genes but also block the expression of CEBPA. See also Figure S7.