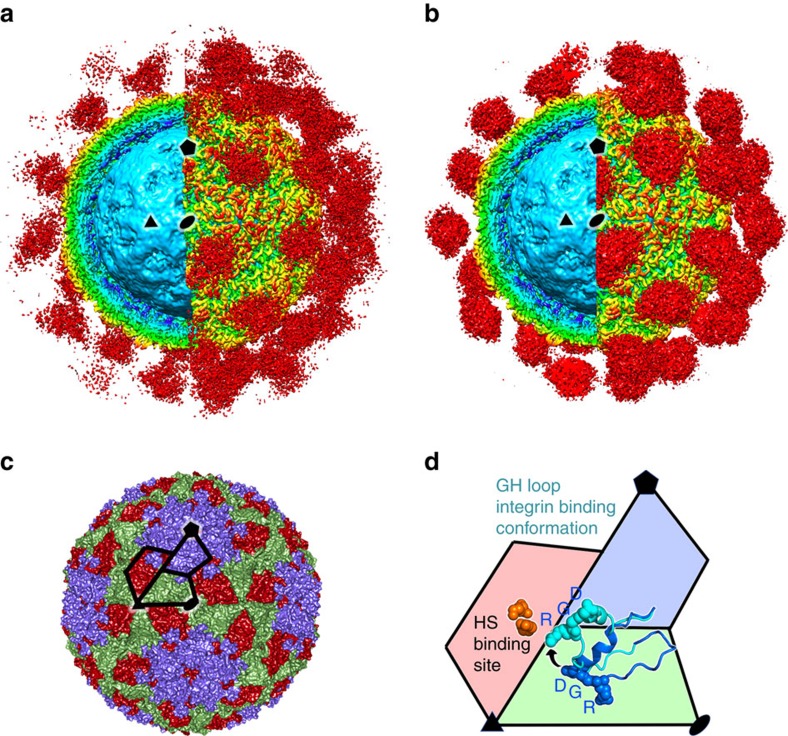
Figure 1. Apo and holo αvβ6-FMDV complexes.
(a) The density for the αvβ6-PanAsia complex determined by cryo-EM. On the left of the image the front half of the density has been cut away so that a cross-section of the binding can be seen. Depth-cueing is used such that colour indicates radius (<110 Å: cyan; 120–140 Å: yellow; >150 Å red). Clouds of red density show the bound integrin. (b) EM structure of αvβ6-O1M, depicted as for a. (c) The structure of PanAsia determined by crystallography. Colouring reflects the different viral proteins, VP1 (blue), VP2 (green) and VP3 (red). One asymmetric unit is outlined. (d) Enlargement of one asymmetric unit coloured as in c. Two conformations of the VP1 GH loop are rendered using a ribbon representation and the RGD motif is depicted with spheres. The conformational change from that seen in reduced O1 virus (PDB:1FOD) (blue) to the integrin bound conformation (cyan) is depicted with an arrow. Some of the residues involved in heparin sulfate (HS) binding are shown as orange spheres and the binding site is labelled. In all panels, one 2-fold, 3-fold and 5-fold axis of icosahedral symmetry has been labelled by a black ellipse, triangle and pentagon, respectively, and all panels show the same view down a 2-fold axis of symmetry.