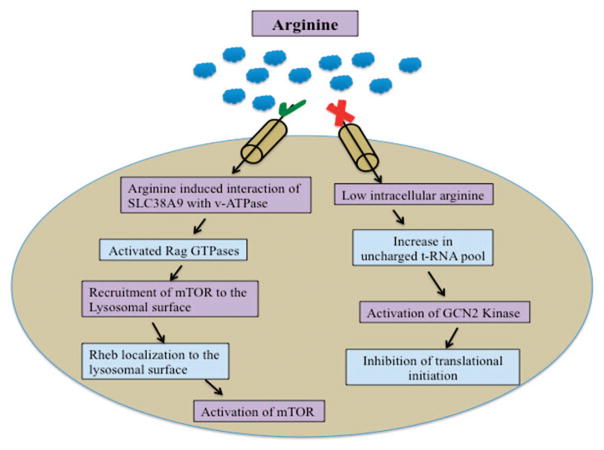
Figure 1.
AAR pathway. Restriction of essential amino acids activates the general control nondepressible protein 2 (GCN2) kinase by increasing uncharged tRNA pool.196 Activated GCN2 kinase phosphorylates the translation initiation factor eIF2α. Phosphorylated eIF2α binds more tightly to eIF2β, inhibiting the exchange of GDP for GTP. Inhibition of GDP exchange for GTP further inhibits the binding of eIF2 complex to methionine aminoacyl tRNA, leading to inhibition of translational initiation.197 Recently, SLC38A9 has been identified as an upstream positive regulator of the mTOR pathway. Amino acids activate the RAG GTPases, which then recruit mTOR to the lysosomal surface. Rheb also localizes to lysosomal membrane. mTOR activation occurs only when both RAG GTPases and Rheb are active. Upon amino acid deprivation, tuberous sclerosis complex translocates to lysosomal surface and promotes GTP hydrolysis by Rheb and thereby inhibiting mTOR complex.164