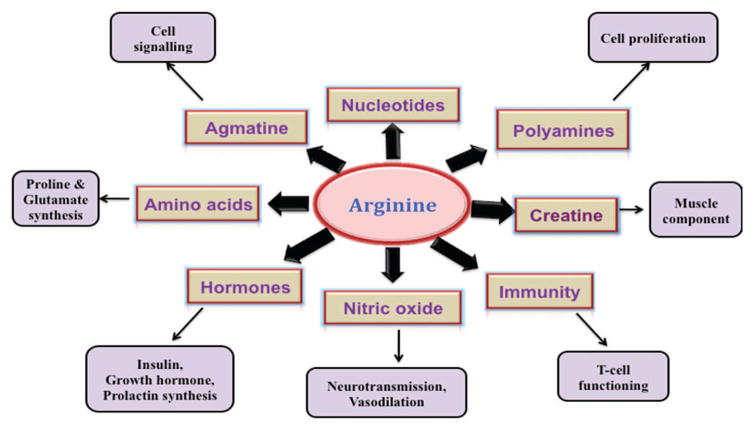
Figure 2.
Involvement of arginine in human physiology. Arginine is a dibasic, cationic amino acid and is considered as ‘conditionally essential’ amino acid. Arginine plays a crucial role in innate and adaptive immunity. For example, increased role of arginine in myeloid-derived suppressor cells results in the impairment of T-cell proliferation and function.190 Arginine has been identified as the sole physiological precursor for NO, a key performer in many cellular regulatory functions. Arginine also is a precursor of two important amino acids, proline and glutamate.198 One of the most important roles of arginine is its implication in the synthesis of polyamines through the diversion from NO synthesis pathway. Polyamines are known to promote tumor growth, invasion and metastasis.199 Arginine also has a vital role in the synthesis of nucleotides, creatine, agmatine and hormones such as insulin and prolactin.200