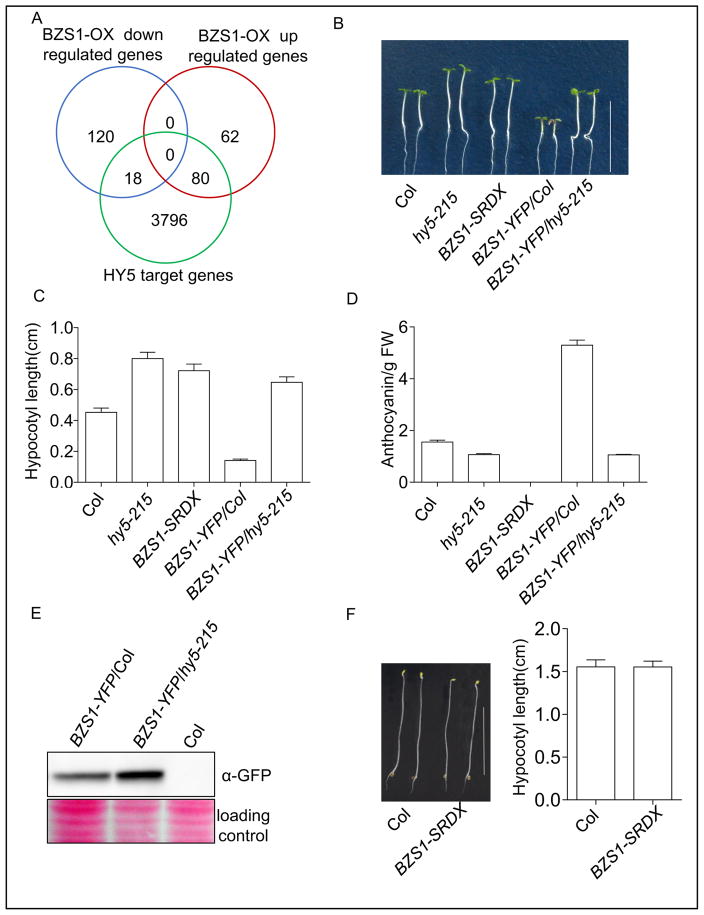
Fig. 2. The function of BZS1 is dependent on HY5.
A: Overlaps of BZS1-regulated genes (Fan et al., 2012) with HY5 target genes (Lee et al., 2007). B: Phenotypes of wild-type (Col), hy5-215, BZS1-SRDX, BZS1-YFP/Col, and BZS1-YFP/hy5-215 seedlings grown under constant red light (20 μmol m–2s–1) for 4 days. Scale bar, 1 cm. C: Hypocotyl length measurement of seedlings described in (B). Error bars represent SD (n = 30). Significant differences are marked as asterisks, P < 0.001. D: Anthocyanin content of the indicated seedlings grown under continuous white light (100 μmol m–2s–1) for 5 days. Error bars represent SD (n = 30). Significant differences are marked as asterisks, P < 0.001. FW, fresh weight. E: Western blot analysis of BZS1 protein accumulation in the hy5 mutant. Total proteins were extracted from 4-day-old seedlings grown under continuous white light (100 μmol m–2s–1). F: Hypocotyl length of BZS1-SRDX seedlings grown in the dark for 4 days. Error bars represent SD (n = 30). Scale bar, 1 cm.