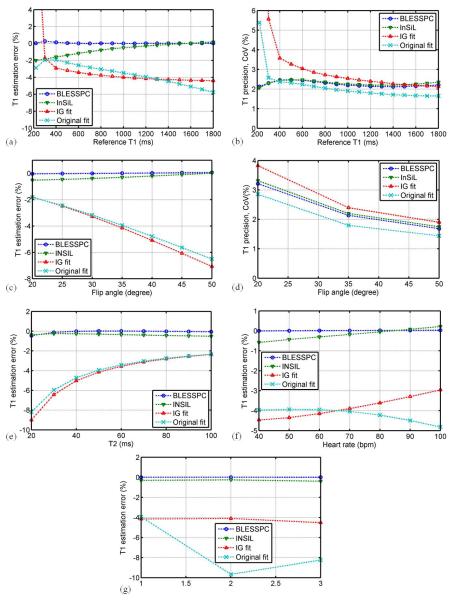
Figure 1.
Simulation - comparison of four T1 estimation algorithms for the MOLLI sequence in terms of (a, b) T1 estimation accuracy and precision for T1 range from 220 ms - 1800 ms, (c, d) T1 estimation accuracy and precision at different radio-frequency excitation flip angles for T1 = 1200 ms, and their sensitivity to tissue T2 variation (e), heart rate variation (f) and acquisition schemes variation (g). The standard acquisition scheme 5(3)3 is used for results from a - f. Overall, BLESSPC and InSiL generated more accurate native myocardial T1 values and were less sensitive to flip angle, tissue T2, and heart rate, and acquisition scheme variations when compared to IG fit and original fit. BLESSPC was slightly better than InSiL. The original fit had superior precision over the other three methods for T1 > 400 ms, while for T1<400 ms, BLESSPC and InSiL were more precise. Using IG fit resulted in much lower precision for T1 < 1000 ms compared to the other three methods. The CoV of IG fit for T1 = 220 ms > 10%, which is out of the display range in (b).