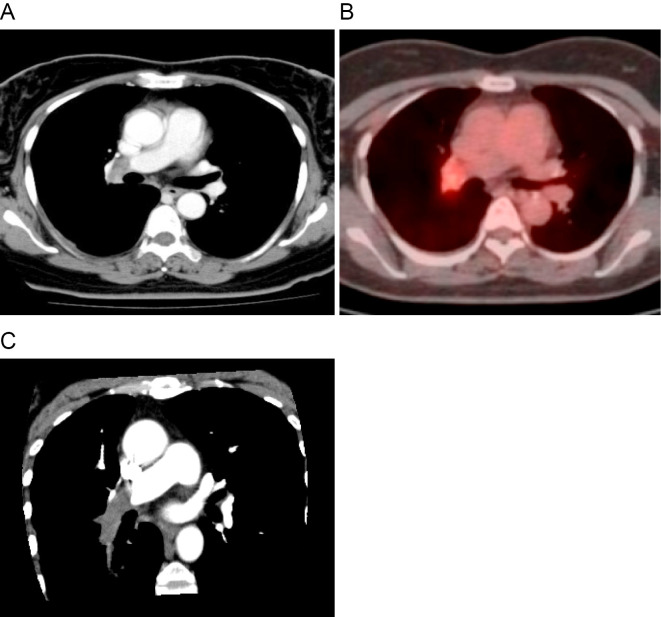
Figure 1.
Radiological examinations. (A) Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) shows a soft-tissue density mass in the right distal main pulmonary artery. (B) 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography with integrated CT shows the mass with a high uptake of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose in the right distal main pulmonary artery. (C) A multiplanar reconstruction image (oblique plane) shows an intravascular mass within the right distal main pulmonary artery that extends to the descending interlobar artery and the segmental branches.