Figure 3.
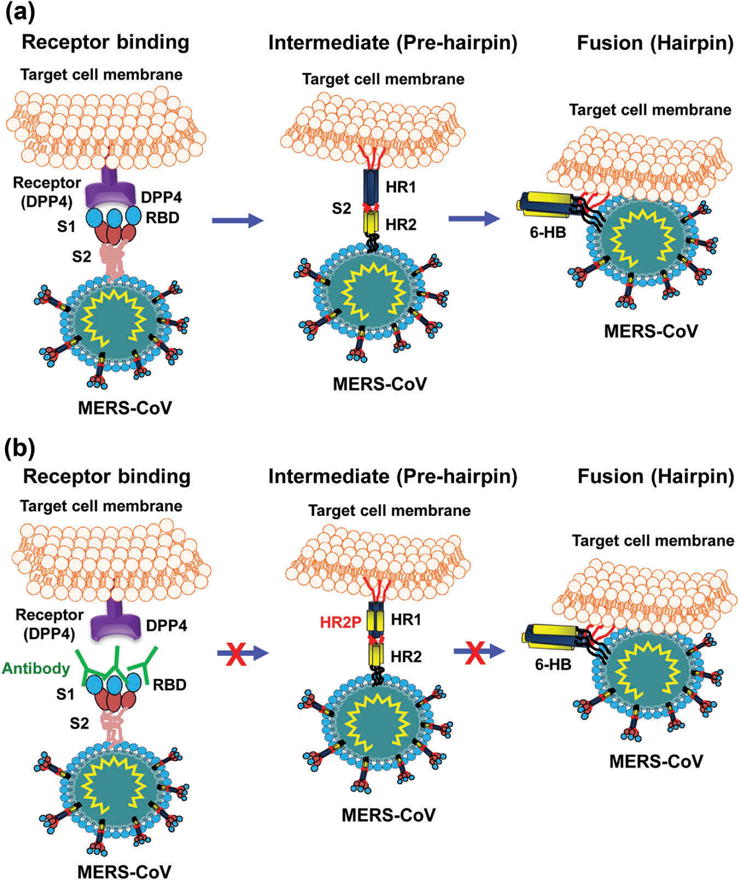
Schematic diagrams of MERS-CoV S protein S2-mediated membrane fusion and MERS-CoV S-targeting mAbs and peptides [59,61]. (a) Schematic diagram of MERS-CoV S2-mediated membrane fusion. The following major processes are involved in MERS-CoV membrane fusion. In receptor binding stage, S protein, which exists as a trimer, binds to the cellular receptor DPP4 via S1-RBD. This binding triggers conformational changes of S protein, leading to dissociation of S1 from S2 with exposed HR1-trimer and HR2-trimer, thus entering intermediate (pre-hairpin) stage. In fusion (hairpin) stage, HR1 and HR2 helices associate with each other to form a 6-helix bundle (6-HB) fusion core, and bring the membranes of virus and cell into close proximity for fusion. (b) Schematic diagram of mechanism of action of MERS-CoV S1-RBD-targeting neutralizing mAbs and S2-HR1-targeting peptides. The RBD-specific antibody (IgG or Fab) binds to viral S1-RBD and interrupts the binding between RBD and DPP4, thus blocking virus infection. HR1-targeting HR2 peptide (e.g. HR2P) binds to the HR1-trimer to form a heterologous 6-HB, thus interferes with subsequent 6-HB fusion core formation and virus-cell membrane fusion, resulting in the inhibition of MERS-CoV infection.
