Figure 4.
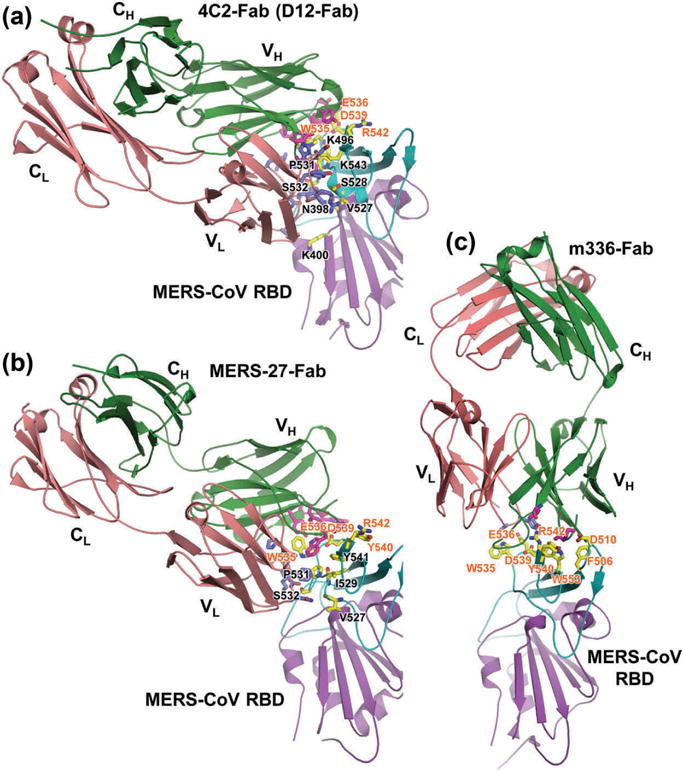
Structural basis of MERS-CoV infection inhibited by RBD-specific neutralizing antibodies [61,69,71,74]. (a) Crystal structures of MERS-CoV RBD in complex with mouse neutralizing mAb 4C2-Fab (PDB ID: 5DO2) or D12-Fab (PDB ID: 4ZPT). Crystal structures of RBD in complex with human neutralizing mAbs MERS-27-Fab (PDB ID: 4ZS6) (b) and m336-Fab (PDB ID: 4XAK) (c). MERS-CoV RBD core structure is colored purple, and RBM is in cyan. The mAb-Fab light (L) and heavy (H) chains are in red and green, respectively. VH, CH, VL, and CL indicate variable heavy, constant heavy, variable light, and constant light chains, respectively. Contacting residues at the RBD-binding interface in Fab-VL and VH chains are shown as blue and magenta sticks, respectively, and those in RBM are shown as yellow sticks. Contacting residues in the RBM involved in both human hDPP4-binding and Fab-binding are labeled in red, and the selected RBD residues at the Fab-binding interface are in black. Full color available online.
