Figure 3.
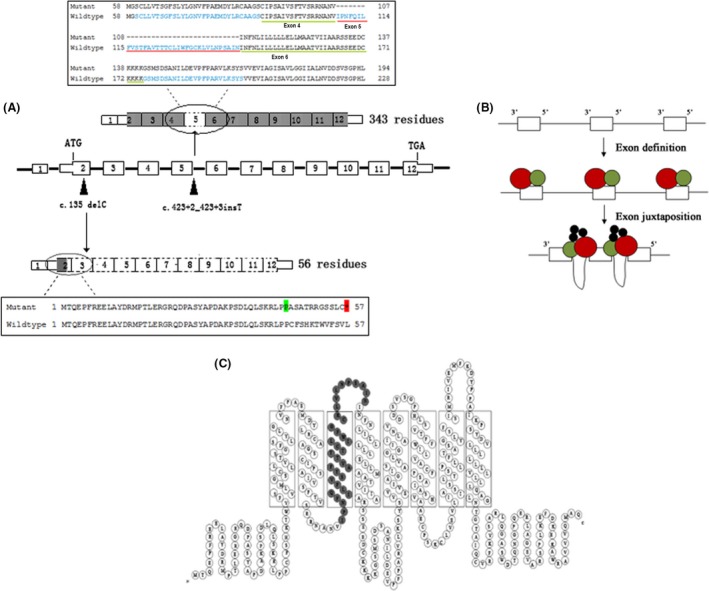
(A) Schematic representation of function patterns for the two mutations. Black arrowheads are mutation positions on MLC1 gDNA (middle). The mutation c.135delC creates an in‐frame stop codon in exon 2 and leads to a truncated protein of 56 residues (black box below). The mutation c.423+2dupT gives rise to an incomplete protein without exon 5 (black box above). Dotted boxes indicate the coding region that is not transcribed. (B) Sketch of “exon definition” with small exons and large introns. Splicing machinery (red and green) interacting with isolated exons during exon definition. Splicing factors (black) join the assembly during the exon juxtaposition following exon definition 11. (C) 2D model of the MLC1 protein 7. The gray parts show the deleted residues of exon 5.
