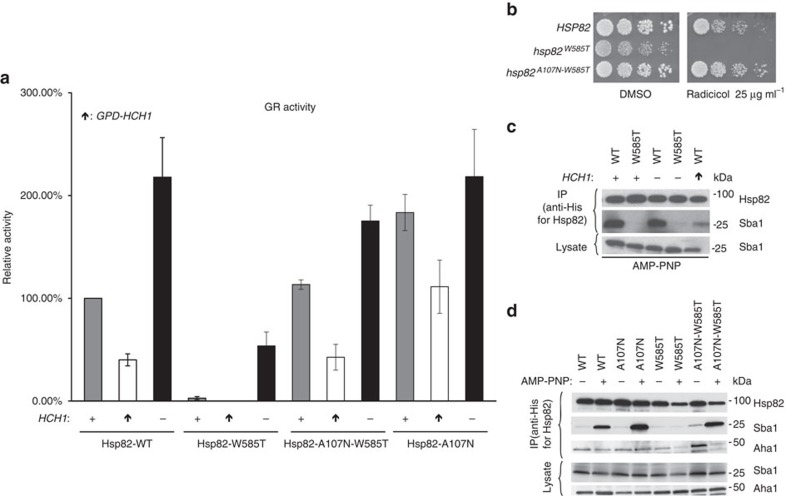
Figure 6. A107N mutant rescues Hsp82-W585T and HCH1 phenotypes.
See also Supplementary Fig. 5. (a) hsc82hsp82 and hch1hsc82hsp82 cells expressing Hsp82 WT (MR923 and MR925), W585T (MR851 and MR858), A107N-W585T (MR852 and MR859) or A107N (AF3 and AF6) were transformed with vector or pRS414GPD-HCH1 (arrow pointing up) as well as a plasmids containing pG/N795-GR and pUCΔSS-26X. These cells were grown to mid-log phase followed by the addition of synthetic hormone. Following a 5-h incubation, β-galactosidase activity was quantified (each sample was run in triplicate and error bars represent s.d. from the mean). These strains were then lysed and analysed using SDS–PAGE and the indicated antibodies. (b) hsc82hsp82 (MR318) cells were transformed with either HSP82 WT, W585T or A107N-W585T constructs. Transformants were struck on to 5-FOA for 2 days, grown overnight in rich media, diluted 10-fold and grown on rich media plates containing DMSO or 25 μg ml−1 of the Hsp90 inhibitor Radicicol and incubated at 30° for 2 days. (c,d) hsc82hsp82 and hch1hsc82hsp82 cells were transformed with the indicated His-tagged Hsp82 constructs as well as vector or pRS414GPD-HCH1 (arrow pointing up). Cells were grown overnight in minimal media and collected. These cells were then lysed and His-complexes were isolated using nickel resin beads in the presence (+) or absence (−) of AMP-PNP. Following SDS–PAGE, His-complexes were analyzed by Western blot with antibodies shown.