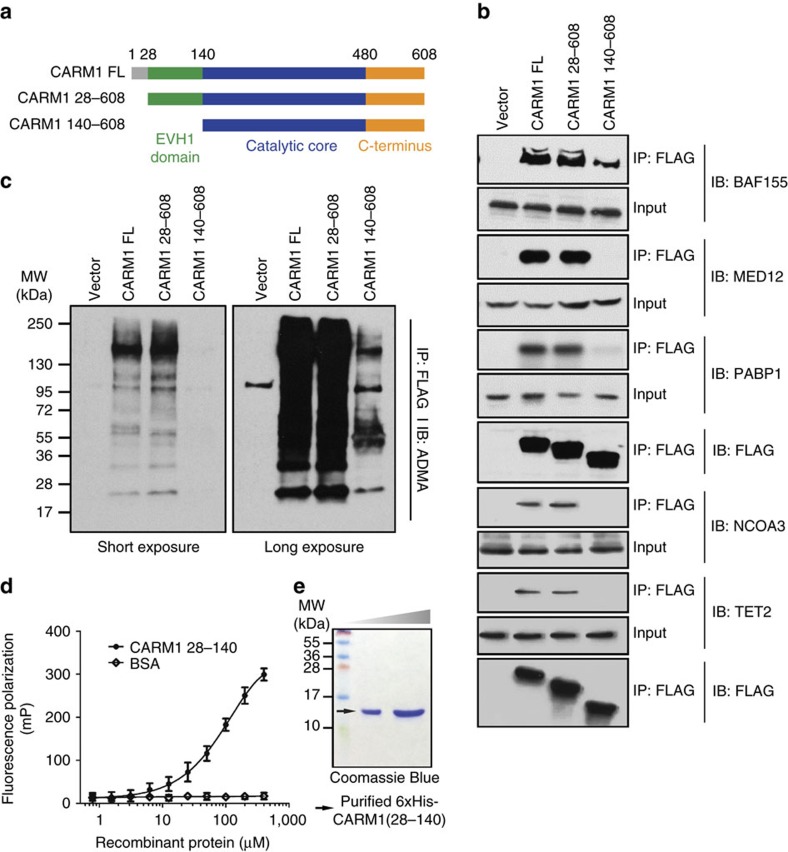
Figure 3. Requirement of the N-terminal domain for substrate recognition by CARM1.
(a) Schematic diagram of FL and N-terminal truncated CARM1 derivatives. CARM1 FL protein contained 608 residues. CARM1 28–608 lacks the first, unstructured 28 residues denoted in grey. CARM1 140–608 lacks the first 140 residues encompassing the EVH1 domain denoted in green. (b) Western blot analyses of co-immunoprecipitated BAF155, MED12, PABP1, NCOA3 and TET2 with FLAG-tagged CARM1, transiently transfected into HEK293T CARM1 KO cells. CARM1 was immunoprecipiated with the anti-FLAG antibody, and the presence of BAF155, MED12, PABP1, NCOA3 and TET2 in the immunoprecipitates was detected with western blots using the respective antibodies. The loading controls are depicted below the corresponding western blot results, separately for BAF155, MED12 and PABP1, and the other two proteins. In all cases the amount of co-precipitated protein was strongly reduced in cell lines expressing N-terminus truncated CARM1 140–608. (c) Western blot analyses of total ADMA-containing proteins co-precipitated with CARM1. The FLAG-tagged CARM1 immunoprecipitates in b were probed with ADMA antibodies. The strong reduction in the levels of ADMA—containing proteins in cells expressing CARM1 140–680 was evident on both short (left) and long exposure (right). The corresponding loading control was shared between the experiments in b (BAF155, MED12 and PABP1) and c and is depicted in b labelled with IB: FLAG. (d) FP assay using purified recombinant 6xHis-CARM1 28–140 and fluorescein-labelled BAF155 peptide. Pronounced increase in FP was observed at high concentrations of recombinant CARM1, but not with the BSA control, demonstrating that the EVH1 domain of CARM1 directly interacts with the enzyme's substrate at low affinity. (e) Coomassie Blue staining of highly purified recombinant 6xHis-CARM1 28–140 used in the FP assay (d).