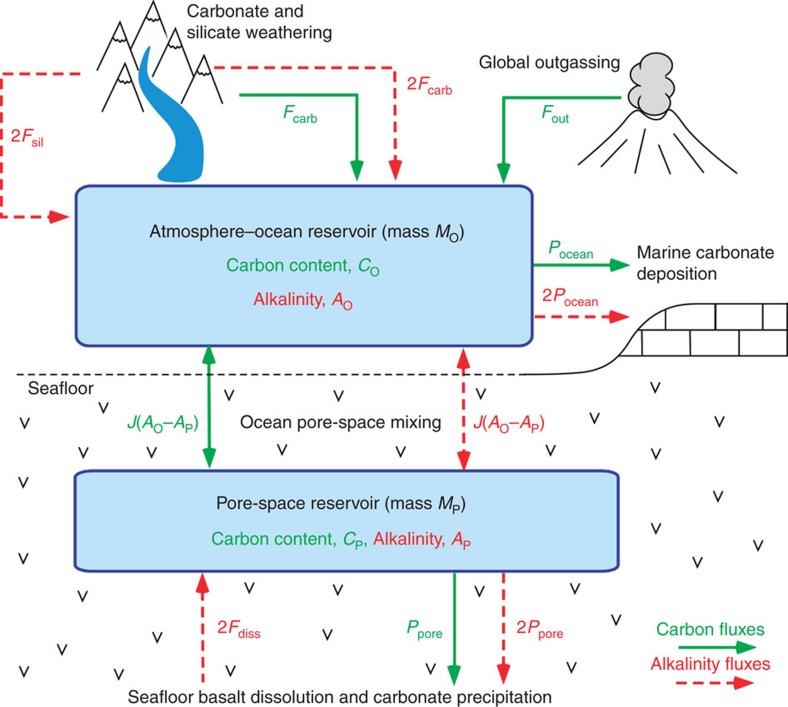
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the box model used in this study.
Carbon fluxes (Tmol C per year) are denoted by solid-green arrows, and alkalinity fluxes (Tmol eq per year) are denoted by red-dashed arrows. The fluxes into/out of the atmosphere–ocean are outgassing, Fout, silicate weathering, Fsil, carbonate weathering, Fcarb, and marine carbonate precipitation, Pocean. The fluxes into/out of the pore-space are basalt dissolution, Fdiss, and pore-space carbonate precipitation, Ppore. Alkalinity fluxes are multiplied by two because the uptake or release of one mole of carbon as carbonate is balanced by a cation with a 2+ charge (typically Ca2+). A constant mixing flux, J (kg per year), exchanges carbon and alkalinity between the atmosphere–ocean and pore-space.