Figure 3. The volasertib/belinostat regimen induces mitotic arrest, frequent mitotic errors and mitotic catastrophe in DLBCL cells.
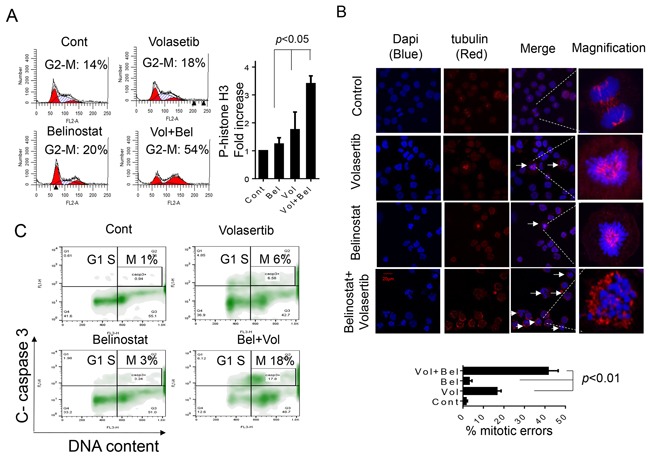
A. SU-DHL4 cells were exposed to 400 nM belinostat and 25 nM volasertib alone or in combination for 30 hr, after which cells were fixed and cell cycle distribution analyzed by flow cytometry (left panel). Cells treated as above were fixed and stained with p-Histone H3. The percentage of p-Histone H3-positive cells was then compared to values for single-agent treatment or untreated controls. (Values indicate fold increases compared to controls; right panel, p < 0.05). B. SU-DHL4 cells were treated as above for 30 hr and immunofluorescence staining performed utilizing antibody directed against α-tubulin (red) and DNA counterstained with DAPI (blue). Arrows indicate cells displaying mitotic errors. High magnification images of a representative cell in each treatment group are shown in the right panels. A total of 100 cells per treatment were enumerated as normal or displaying mitotic errors including multi-polar spindles, improper tubulin alignment, or defective cytokinesis. The percentage of mitotic errors cells was determined and displayed in the lower panel with values for combined treatment significantly greater than those for control or single-agent treatment; p < 0.01. C. The distribution of apoptotic SU-DHL4 cells in various cell-cycle phases following treatment with volasertib ± belinostat as above was then determined by combining staining for cleaved caspase-3 and DNA content (PI). Representative results are shown indicating caspase-3 activation in specific cell-cycle phases, including G2M.
