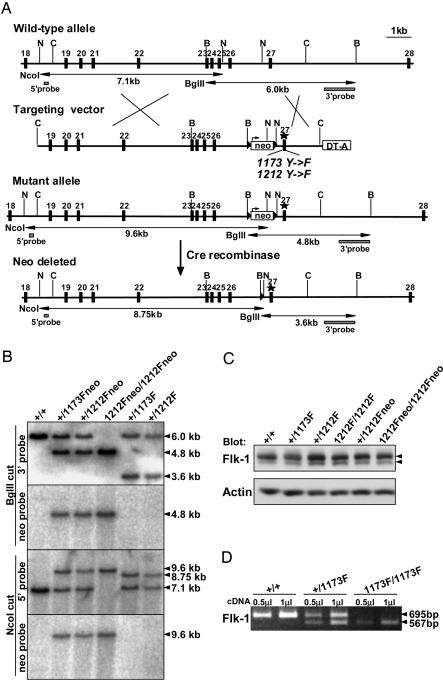
Fig. 1.
Generation of Flk-1 knock-in mutant mice. (A) Targeting strategy. B, BglII; C, ClaI; N, NcoI. LoxP sites are indicated by triangles. (B) Southern blot analysis of tail genomic DNA from wild-type (+/+), Flk-1+/1173Fneo, Flk-1+/1212Fneo, Flk-11212Fneo/1212Fneo, Flk-1+/1173F, and Flk-1+/1212F mice. Tail genomic DNA was digested with BglII and hybridized with a 3′ probe and neo probe, or digested with NcoI and hybridized with a 5′ probe and neo probe. (C) Western blotting of lung lysates from adult mice with anti-Flk-1 antibody. Arrowheads indicate Flk-1 proteins. Anti-actin antibody was used as a control to verify that an equivalent amount of protein was loaded in each lane. (D) RT-PCR analysis of wild-type (+/+), Flk-1+/1173F, and Flk-11173F/1173F E8.5 embryos. PCR was performed by using 0.5 μlor1 μl of cDNA in 20-μl reactions by Flk-1 primers coding exons 22–28. The PCR products were digested with AccIII, which digests only the 1173F mutant PCR products. The undigested, 695-bp product represents the mRNA expressed from the wild-type allele, and the digested 567-bp product represents the mRNA expressed from the 1173F mutant allele.