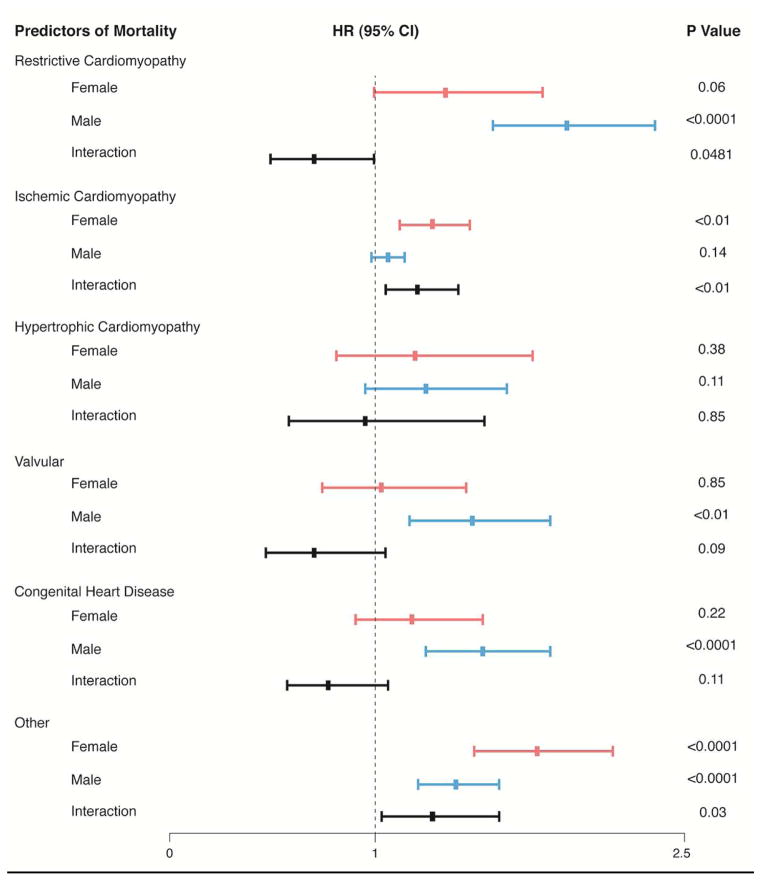
Figure 2. Sex Differences in Survival Based on Type of Heart Disease.
The risk of being female or male with a given type of heart disease while awaiting heart transplantation was assessed by multivariate Cox proportional hazard analyses adjusting for sex, age, race, insurance, body mass index, ABO blood type, hypertension, Era, tobacco usage, diabetes mellitus, malignancy, prior cerebral vascular accident, peripheral vascular disease, dialysis, estimated glomerular filtration rate, albumin, mean pulmonary arterial pressure, cardiac index, implantable cardioverter defibrillator, mechanical ventilation, intra-aortic balloon pump, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, ventricular assist device, total artificial heart, and inotropes. The analyses also included possible interactions between female sex and type of heart disease.
CHD=congenital heart disease, DCM=dilated cardiomyopathy, HCM=hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, ICM=ischemic cardiomyopathy, RCM=restrictive cardiomyopathy, valvular=valvular heart disease, and Other=(1216 prior heart transplants and 312 “other”)