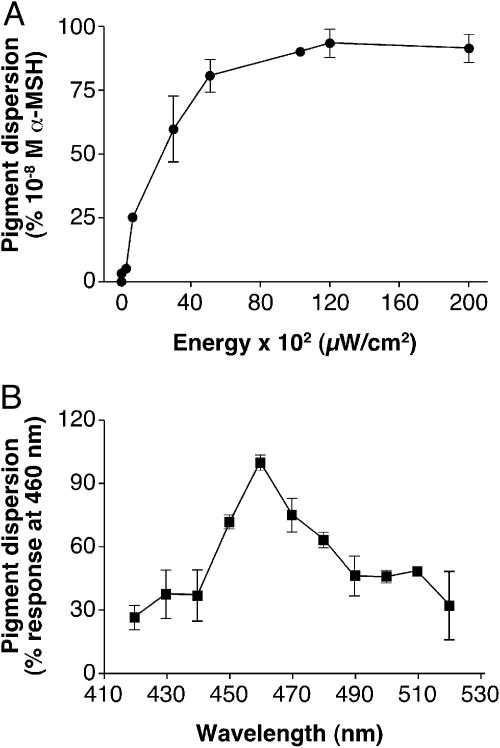
Fig. 1.
Xenopus melanophores were seeded in 96-well plates and kept in the dark for a minimum of 3 days. Before the assay, the cells were incubated with 10–9 M melatonin for 90 min to fully aggregate the melanosome. (A) Cells were exposed to increasing intensities of white light, and the photoresponse, melanosome dispersion, was quantified as absolute absorbance in a plate reader and expressed as the percentage of the absorbance of cells treated with 10–8 M α-MSH (considered as 100%), a potent melanosome-dispersing hormone. The EI50 was determined to be 20.82 × 102 μW/cm2. This nonsaturating irradiance was used in all pharmacologic assays. Each point is the mean ± SE (n = 6) at the irradiance values noted. (B) Cells were exposed to a range of wavelengths, and melanosome dispersion was quantified as the absolute absorbance and expressed as the percentage of the absorbance of cells irradiated with 460 nm (considered as 100%). The number of photons was kept constant (1 × 1018 s–1·cm–2). Each point is the mean ± SE (n = 6) at the wavelength noted.