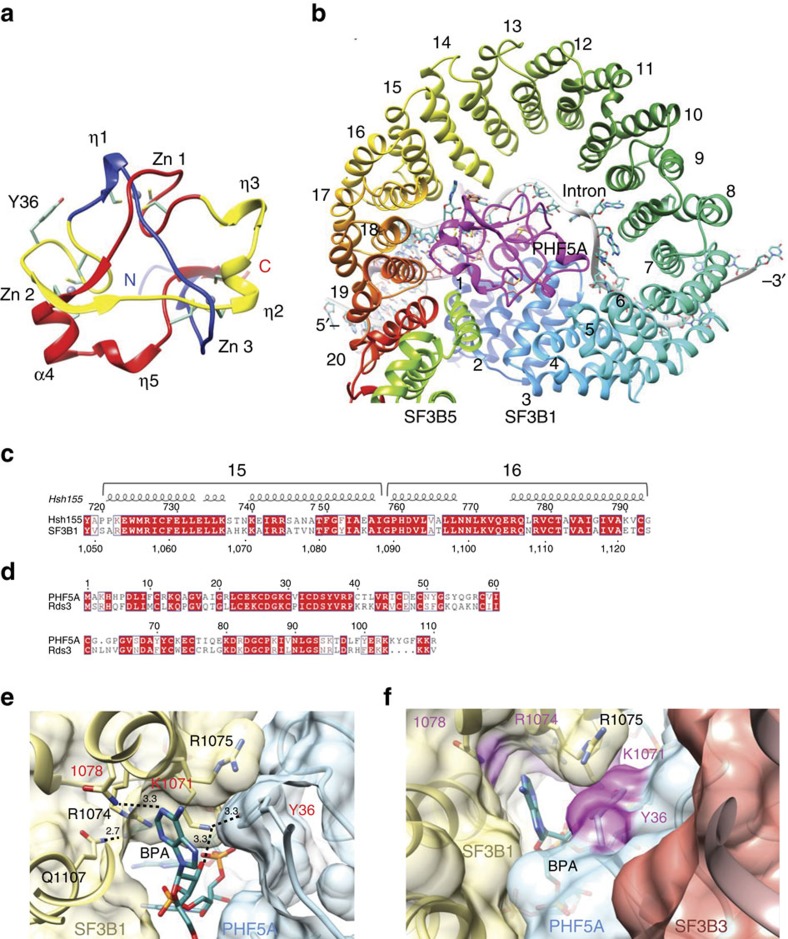
Figure 6. Crystal structure of human PHF5A.
(a) Ribbon diagram of PHF5A (PDB:5SYB). Zinc atoms are shown as grey balls and form the vertices of a near equilateral triangle. The secondary structural elements (α: helix, η:310 helix, β: strand) forming the sides of the trefoil knot are coloured blue, yellow and red arranged by their primary sequence. The N and C termini are labelled. Cysteine residues are shown as sticks as well as the critical Y36 residue. (b) Model of PHF5A in the yeast Bact complex. Yeast PHF5A (magenta), SF3B5 (neon green) and SF3B1 (rainbow colours according to HEAT repeat HR-1 to 20) formed a complex that made contacts to the RNA duplex base-paired by U2 snRNA (orange ribbon) and the branch point sequence (BPS), and as well as a single-stranded intron RNA at the downstream of BPS (grey ribbon and the atoms are coloured in cyan). (c) Sequence alignment of the HEAT repeat 15 and 16 where this part of Hsh155 formed adenine-binding site with Rds3. (d) Sequence alignment of PHF5A with Rds3. The sequence identity is 56%. (e) Potential configuration of human adenine-binding site showing interactions between PHF5A (light blue), SF3B1 (yellow) and intron RNA (cyan). (f) Surface view of the potential modulator-binding site composed by SF3B1 (yellow), PHF5A (light blue) and SF3B3 (orange). Drug-resistant residues were highlighted in magenta.