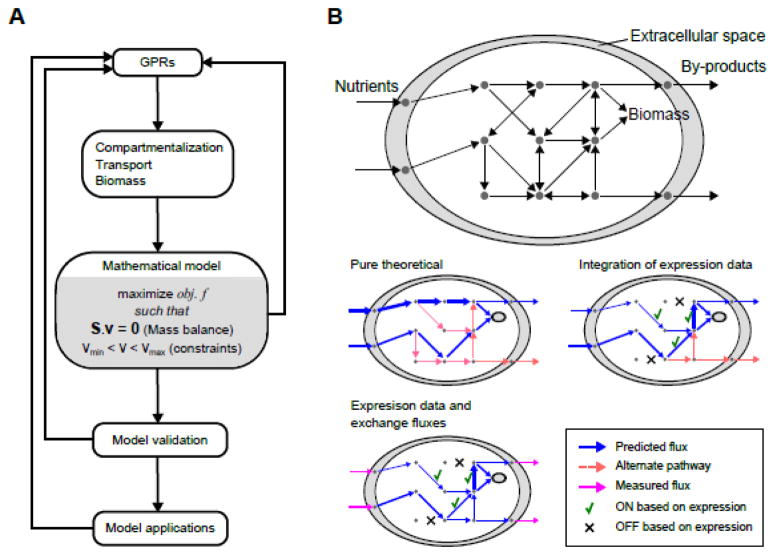
Figure 2.
Genome-scale metabolic network modeling. (A) Metabolic network modeling is an iterative procedure. Main steps of model development are shown. (B) Cartoon representation of a GSMNM (top) and flux balance analysis (middle and bottom). In the absence of experimental constraints, pure theoretical analyses can be done (middle left). A flux distribution is found but alternate pathways exist. Integration of gene expression data guides the flux distribution to choose from alternate pathways (middle right). Still, alternate solutions may exist. Inclusion of experimental measurements for exchange fluxes can constrain the solution further (bottom left).