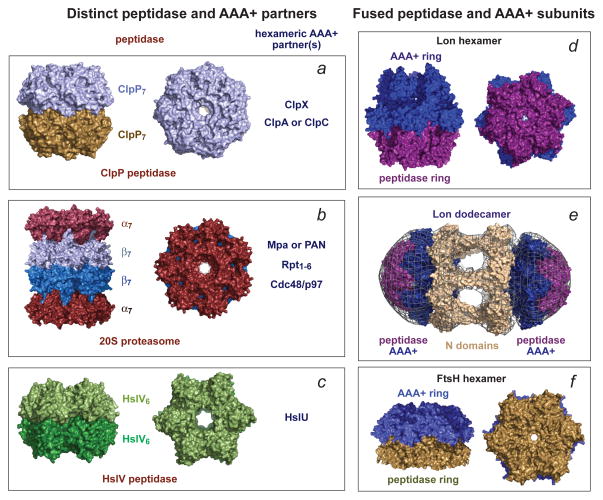
Figure 1. Self-compartmentalized peptidases are the degradation components of AAA+ proteases.
In each panel, a single representative structure is shown. (a) The ClpP peptidase from E. coli (pdb 1TYF) consists of two heptameric rings, uses a Ser–His–Asp catalytic triad for peptide-bond cleavage, and functions with one of three homohexameric AAA+ partners (ClpX, ClpA, or ClpC). In different species, ClpP can consist of 14 identical subunits, distinct homomeric rings or a mixture of subunits in each ring. (b) The 20S proteasome from Thermoplasma acidophilum (pdb 1PMA) has an α7β7β7α7 structure, uses a Thr nucleophile for peptide-bond cleavage, and partners with homohexameric Mpa in bacteria, homohexameric PAN or Cdc48/p97 in archaea, or the heterohexameric Rpt1–6 ring in the eukaryotic 26S proteasome. The α and β rings have seven identical subunits in bacteria and archaea and seven distinct α or β subunits in eukaryotes. (c) The HslV peptidase from Haemophilus influenzae (pdb 1G3I) consists of two homohexameric rings (each subunit is homologous to a β subunit of the 20S proteasome), uses a Thr nucleophile for peptide-bond cleavage, and partners with an HslU homohexamer. (d) The homohexameric Lon protease from Thermococcus onnurineus (pdb 3K1J) is assembled from subunits in which the AAA+ module is fused to the peptidase domain and uses a Ser–Lys dyad for peptide-bond cleavage. (e) Two E. coli Lon hexamers can combine to form a dodecamer, which is stabilized by N-domain interactions that form portals of ~45 Å into the enzyme lumen. The panel shows the E. coli 3LJC and B. subtilis 3M6A structures modeled into a low-resolution electron-density map91. (f) The homohexameric Thermotoga maritima FtsH protease (pdb 3KDS) also assembles from subunits in which the AAA+ module is fused to the peptidase domain. FtsH uses an Asp–Zn++ active site for peptide-bond hydrolysis.