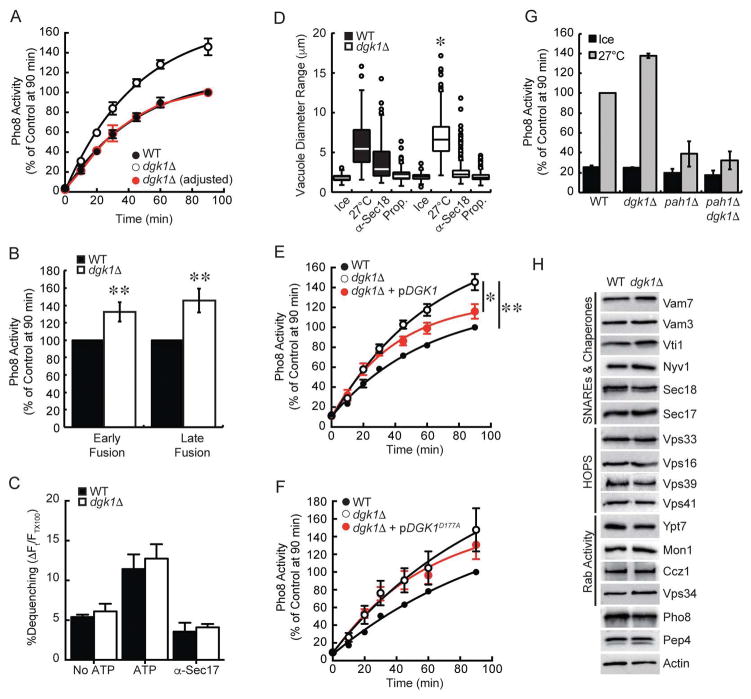
Figure 3. Dgk1 suppresses vacuole fusion.
(A) Fusion reactions were performed using wild type and dgk1Δ vacuoles. Reactions were incubated at 27°C for the indicated times and assayed for Pho8 activity. The red trace represents dgk1Δ fusion when normalized to its own maximum. This reveals the rate of dgk1Δ vacuole fusion versus wild type. (B) The ratio of effector and reporter vacuoles were altered to show early versus late rounds of fusion. To show early rounds of fusion an excess of effector vacuoles (5 μg PEP4 pho8Δ) were incubated with 1 μg of reporter vacuoles (pep4Δ PHO8). To show late rounds of fusion, an excess of reporter vacuoles (4 μg pep4Δ PHO8) were incubated with 2 μg of effector vacuoles (PEP4 pho8Δ). (C) Lipid mixing assay were performed with wild type or dgk1Δ vacuoles. Reporter vacuoles (2 μg) labeled with Rh-PE were incubated with 16 μg of unlabeled vacuoles. Fluorescence (λex=544 nm; λem=590 nm) was measured every 60 sec for 40 min. Shown is the average lipid mixing at 40 min. (D) Measurement of vacuole diameters after incubation (27°C, 90 min). Fusion reactions were treated with PS buffer, 12 μg/ml anti-Sec18, or 2 mM propranolol (Prop.). Measurements were plotted as a box plot representing median vacuoles with upper and lower quartile values. The lines extending from the boxes represent the minimum and maximum vacuoles in the data set. Outliers are displayed as points. (E–F) Fusion assays were performed with vacuoles from wild type, dgk1Δ, or dgk1Δ strains complemented with pDGK1 or pDGK1D177A. (G) Endpoint fusion efficiency was compared between wild type, dgk1Δ, pah1Δ, and pah1Δ dgk1Δ vacuoles. (H) Analysis of fusion components. Vacuoles were isolated from wild type BJ3505 and RFY17 (BJ3505 dgk1Δ) (5 μg protein) and immunoblotted with antibodies against the indicated proteins. To examine the effect of deleting DGK1 on Pep4 trafficking, vacuoles were examined from DKY6281 and RFY18 (DKY6281 dgk1Δ). Error bars represent S.E.M. (n≥3). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 (one-way ANOVA).