Figure 2.
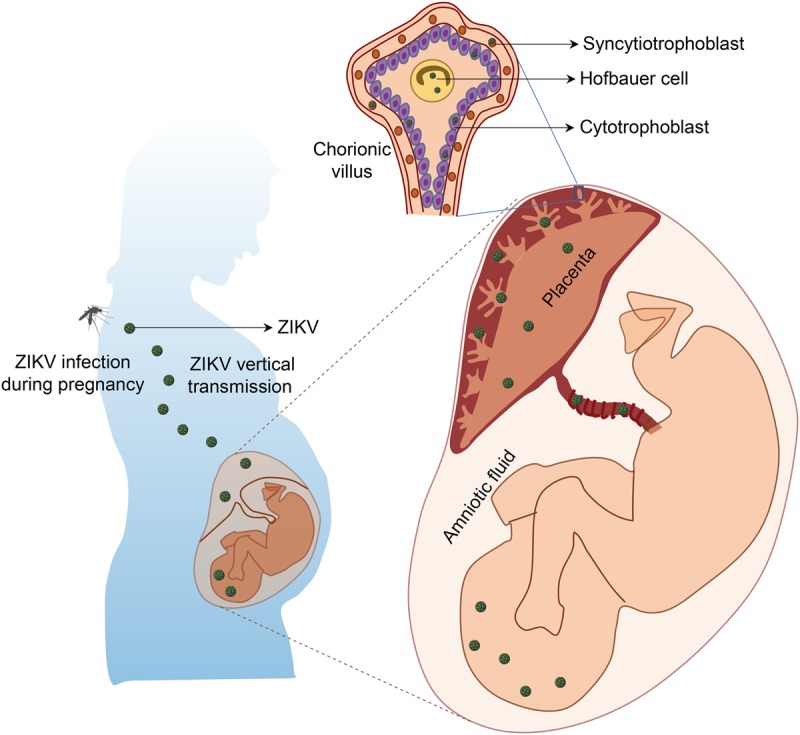
Vertical transmission of ZIKV and its impact on human fetal development. ZIKV could be transmitted to a pregnant woman via the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito, which could be further vertically transmitted from the infected mother to the fetus by infecting placental trophoblasts and macrophages (Hofbauer cells) and crossing the placental barrier.
