Figure 3.
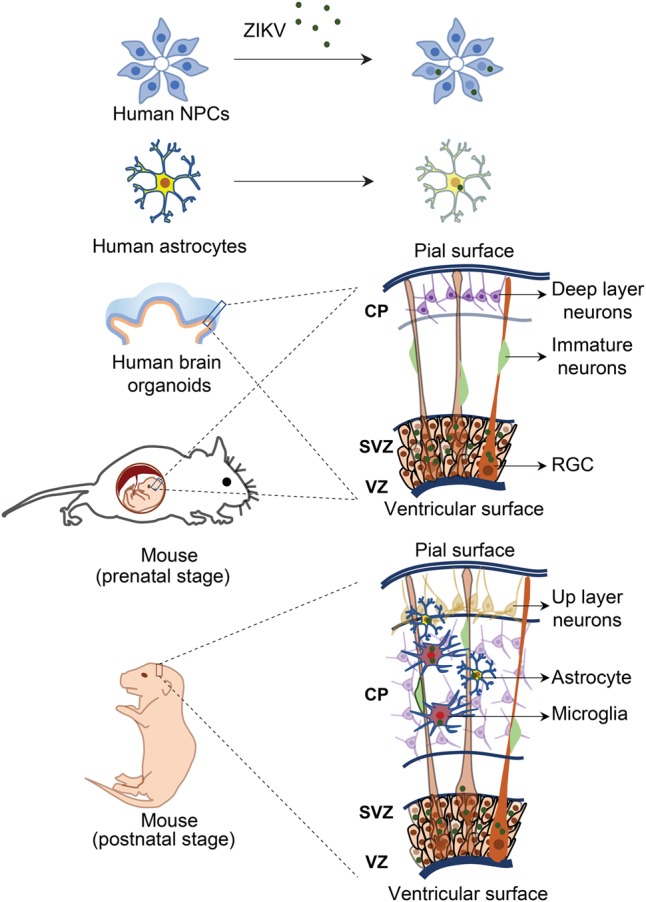
Investigation of neurotropism of ZIKV infection in vitro and in vivo. The effects of ZIKV on brain development and the underlying mechanisms could be explored with in vitro models, such as NPCs, astrocytes, and three-dimensional (3D) brain organoids derived from either hiPSCs or primary human brain tissue, or in vivo animal models, such as mouse models at multiple developmental stages (i.e., prenatal and postnatal stages) by infection of ZIKV through subcutaneous inoculation, intravenous injection, or intraperitoneal injection in pregnant immune-competent mice or direct injection of ZIKV into developing fetal mouse brains.
