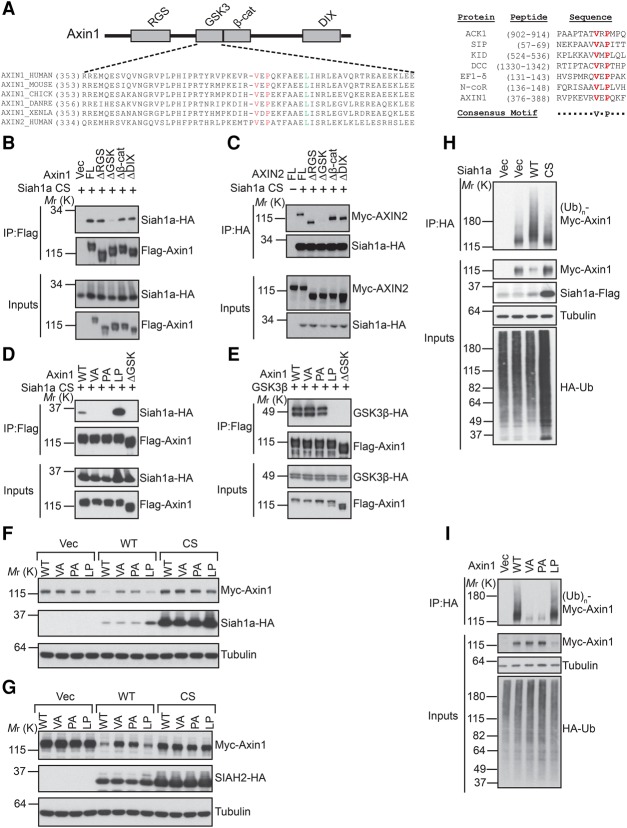
Figure 3.
SIAH1/2 interact with the GSK3-binding domain of Axin and promote its ubiquitination. (A, left panel) A schematic diagram of the domain structure of Axin with the alignment of the GSK3-binding domain of Axin proteins from different species. Val and Pro residues involved in SIAH interaction are highlighted in red, and the Leu residue critical for GSK3 interaction is highlighted in green. (Right panel) Alignment of SIAH1-binding motifs of various SIAH1 substrates. (B,C) The GSK3-binding domain of Axin is required for the interaction with Siah1a. Flag-Axin1 or Myc-AXIN2 was coexpressed with the HA-Siah1a CS mutant in HEK293 cells and subjected to coimmunoprecipitation assay. (D,E) V383A or P385A mutation of Axin1 disrupts Axin1–Siah1a interaction without affecting Axin1–GSK3β interaction. (F,G) Mutation of the SIAH-binding motif attenuates Siah1a-induced Axin1 degradation. (H) Overexpression of wild-type Siah1a, but not its RING domain mutant, promotes Axin1 ubiquitination in vivo. (I) Mutation of the SIAH-binding motif blocks Siah1a-induced ubiquitination of Axin1.