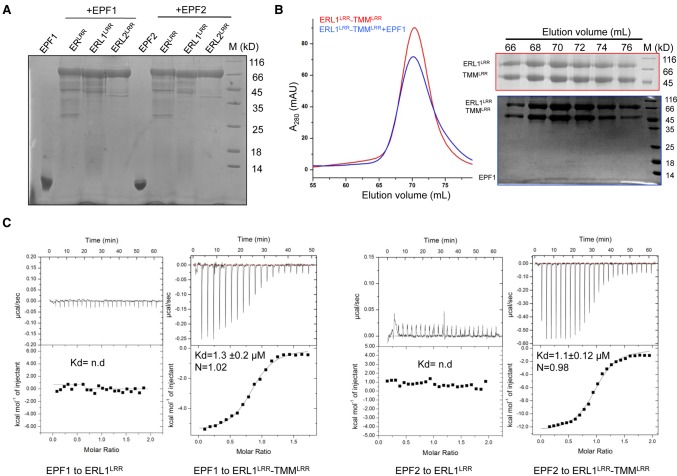
Figure 3.
ERL1–TMM complexes function as receptors of EPF1 and EPF2 in vitro. (A) ERfs alone fail to interact with EPF1 or EPF2 in pull-down assays. The 6xHis-tagged ERLRR, ERL1LRR, and ERL2LRR were incubated individually with EPF1 or EPF2, and the mixtures were then flowed through Ni-NTA beads. After extensive washing, the bound proteins were eluted and analyzed with SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. (B) EPF1 directly binds to the ERL1LRR–TMMLRR complex. (Left panel) Size exclusion chromatography analysis of the interaction between EPF1 and ERL1LRR–TMMLRR; the elution volumes and the molecular weight markers are indicated at the top. (Right panel) SDS-PAGE analysis of peak fractions from the left panel. (C) Quantification of the binding affinity of EPF1 (left) or EPF2 (right) to ERL1LRR or ERL1LRR–TMMLRR by ITC. (nd) No detectable binding. EPF1 or EPF2 was titrated into ERL1LRR or ERL1LRR–TMMLRR protein in the ITC cell. Integrated heat measurements from ITC are shown. The calculated stoichiometry (N) and the dissociation constant (Kd) are indicated.