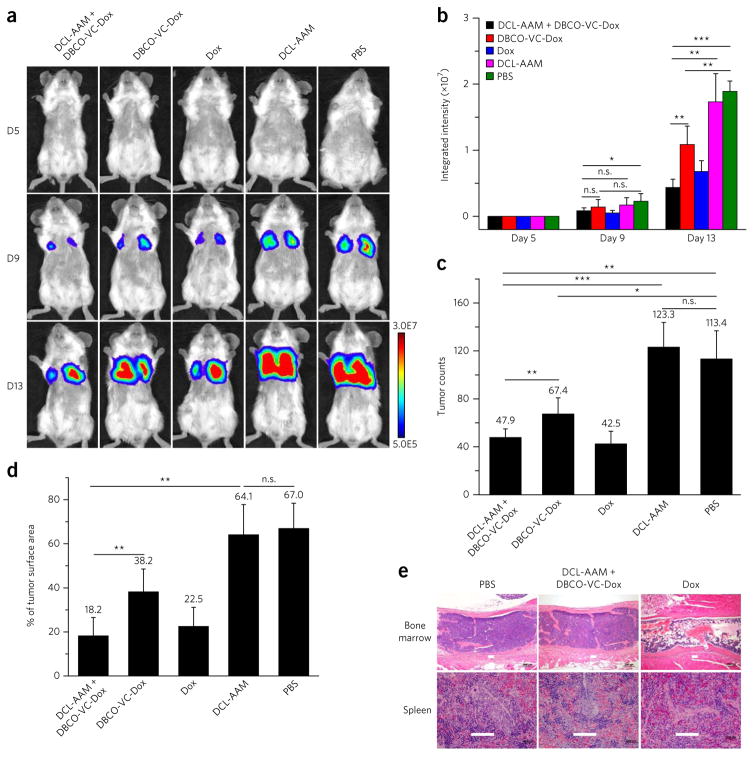
Figure 6. DCL-AAM-mediated tumor labeling improved anticancer efficacy of DBCO–drug conjugate against 4T1 lung metastases.
4T1 lung metastases were established in BALB/c mice by i.v. injection of luciferase-engineered 4T1 cells on day 0, and mice were randomly divided into five groups (group 1: DCL-AAM + DBCO-VC-Dox; group 2: DBCO-VC-Dox; group 3: Dox; group 4: DCL-AAM; group 5: PB S; DCL-AAM + DBCO-VC-Dox, DBCO-VC-Dox and Dox group, n = 8; DCL-AAM and PBS group, n = 7). DCL-AAM (60 mg/kg) was injected i.v. once daily on days 1, 2 and 3. Subsequently, DBCO-VC-Dox (12 mg/kg) or Dox (7.5 mg/kg) was injected i.v. on days 4, 8 and 12. Tumor growth was monitored by bioluminescence imaging on days 5, 9 and 13. (a) Representative bioluminescence images of BALB/c mice on days 5, 9 and 13 (D5, D9, D13, respectively). (b) Average integrated bioluminescence intensity of mice over the course of the efficacy study (n = 7 or 8). (c) Average tumor nodule counts on the lung tissues of mice (n = 7 or 8). (d) Percentage of tumor surface area over total lung tissue area for mice from different groups (n = 7 or 8). (e) Histopathology of BALB/c mice tissues harvested at the end of 4T1 lung metastases efficacy study showed severe toxicity of Dox (22.5 mg/kg in total) in bone marrow (upper row, marked bone marrow lysis) and spleen (lower row, lymphoid depletion), while DCL-AAM + DBCO-VC-Dox (36.0 mg/kg Dox in total) showed minimal toxicity. Scale bar, 100 μm. All the numerical data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. and analyzed by one-way ANOV A (Fisher; 0.01 < *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001).