Figure 7.
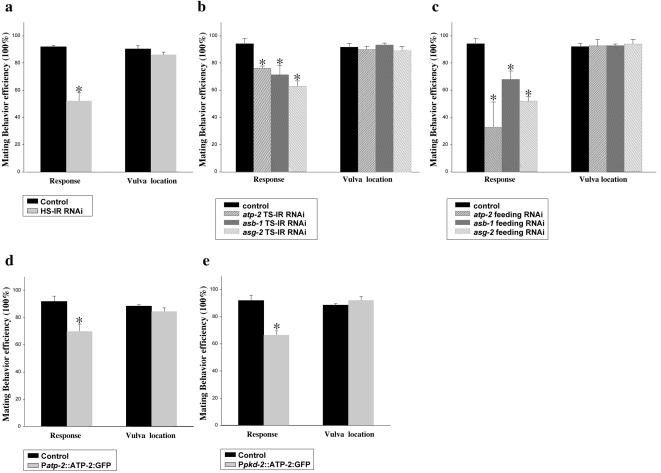
atp-2 and MRC complex V are required for response behavior. (a-c), Knocking down atp-2 and MRC complex V components in wild-type C. elegans males by RNAi affects the response step of mating behavior, but not vulva location. RNAi and mating behavior were performed as described in Materials and Methods. (a) HS-IR RNAi, 1.3-kb inverted-repeat atp-2 cDNA was cloned into pPD49.78 heatshock vector. (b) TS-IR RNAi IR fragments of the atp-2, asb-1, and asg-2 cDNAs were cloned downstream of 1.3-kb pkd-2 promoter. (c) Feeding RNAi, bacterial strains of the atp-2 feeding RNAi clone (III-2B16), asb-1(III-2E22), and asg-2(I-4E04) were obtained from MRC geneservice (Cambridge, United Kingdom). (d and e) Overexpression of atp-2 in wild-type males leads to a defect in the response, but not vulva location, step of mating behavior. (d) A 1.5-kb atp-2 promoter was used to drive the broad expression of atp-2 cDNA. (e) A 1.3-kb pkd-2 promoter was used to drive the expression of atp-2 cDNA in only male-specific neurons. In all experiments, at least 24 animals were blindly scored per trial. For each line, experiment trials were done in triplicate trials to obtain statistical data. Figures were generated using Sigmaplot5 (SPSS). Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Asterisk, p < 0.05 compared with control.
