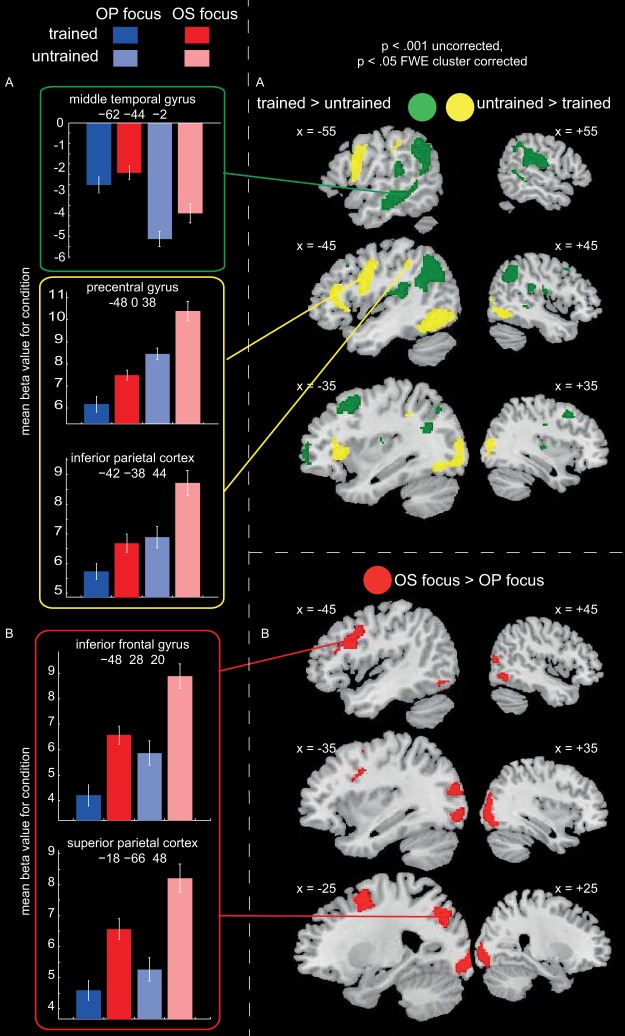
Figure 10.
Brain activity during reading aloud in MRI Scan 2 at the end of training. Slices show main effects from an ANOVA that included the factors lexicality (trained vs. untrained) and training focus (OP vs. OS), which was conducted on activation during see-think trials, for items that were read aloud correctly. Whole-brain activations are presented at p < .001 voxelwise uncorrected and p < .05 FWE cluster-corrected for 20 participants. (A) Slices show main effect of lexicality, green = trained > untrained, yellow = untrained > trained. (B) Slices show main effect of training focus, red = OS > OP focus. Note that no brain regions showed more activation for the OP than the OS focus language. Plots for A and B show see-think activation for trained (dark bars) and untrained items (light bars) for the OP (blue bars) and the OS (red bars) focus languages, at representative peak voxels that showed greater activity for trained than untrained items (green box), untrained than trained items (yellow box), or the OS relative to the OP focus language (red box).