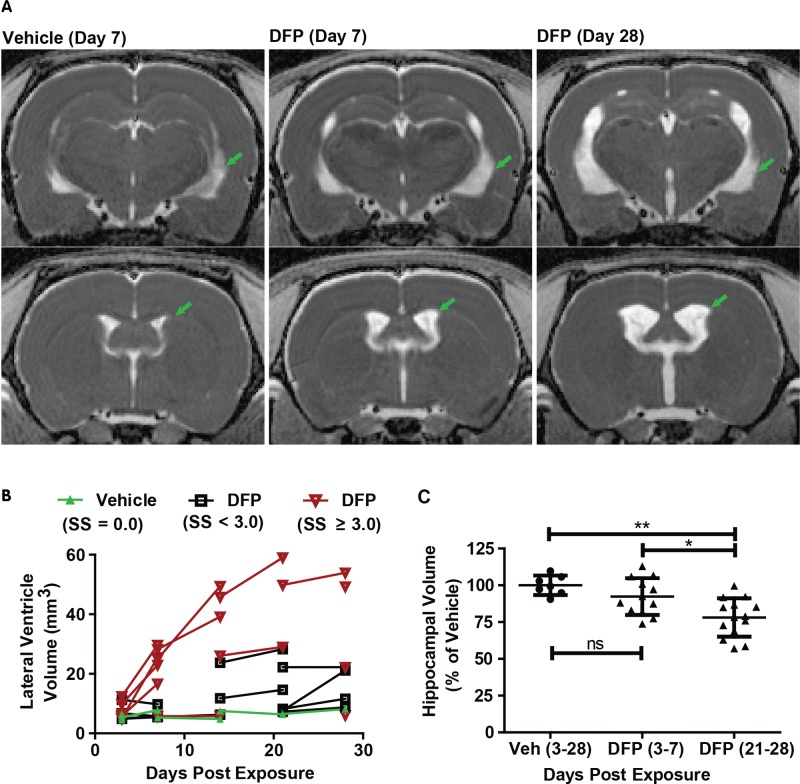
FIG. 3.
Acute DFP intoxication results in delayed ventriculomegaly and hippocampal atrophy. A, Representative, parametric maps of ADC at the level of the hippocampus (top) and caudate putamen (bottom) displaying ventricular enlargement (green arrows). B, Trajectory plots illustrating the effect of day postexposure and initial seizure severity on ventricular volume. Data points connected by line segments indicate repeated scans within a single animal. Vehicle (VEH) controls (green triangles) show no change in ventricular volume over time (slope = 0.07; P = 0.26). DFP animals with average seizure severity (SS) < 3 (black boxes) or ≥ 3 (red inverted triangles) exhibit significant growth of ventricular volume compared with VEH animals (P < 0.015); however, DFP animals with SS ≥ 3 experience growth at a faster rate than their lower seizure severity peers (P = 0.03). C, Hippocampal volume is significantly reduced following DFP exposure (P < 0.05 after Tukey HSD), although this effect is not apparent until three weeks post exposure. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns = no significant difference.