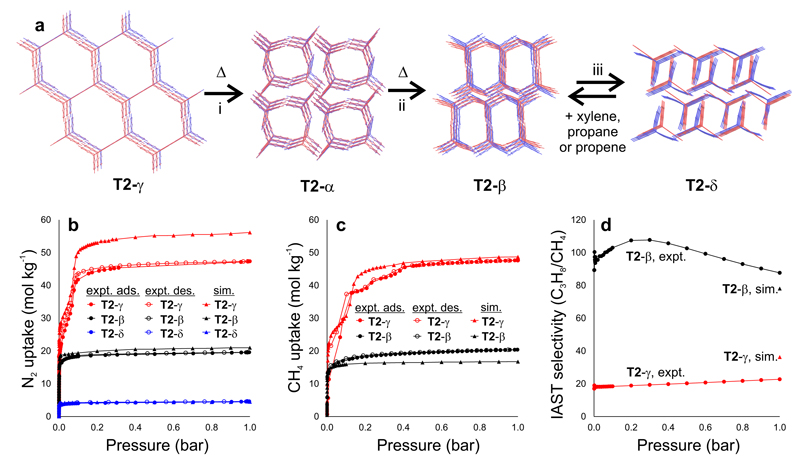
Figure 4. Predicted and experimental structures and gas adsorption isotherms for polymorphs of T2.
a, Overlays of predicted (red) and experimental (blue) structures for T2-γ, T2-α; T2-β; and T2-δ, ordered by increasing predicted density; the transformation conditions for interconverting these polymorphs were as follows: i: loss of solvent at RT, heating at 340 K or mechanical grinding at RT; ii: 358–383 K; iii: direct removal of DMSO and then acetone from DMSO/acetone solvate. All four phases can be isolated as stable solvent-free frameworks in the laboratory. b,c, Predicted and experimental gas adsorption isotherms for T2-γ (red), T2-β (black) and T2-δ (blue). b, nitrogen (77 K) and c, methane (115 K); adsorption = filled symbols; desorption = unfilled symbols. All simulations were performed using the CSP structures. d, Pressure-dependent IAST selectivity of propane over methane determined for equimolar mixtures, using experimental isotherms at 298 K (Fig. S19). The ESF selectivity predictions (Fig. 4d) are marked as upper triangles and colored accordingly for T2-β (black) and T2-γ (red).