Figure 1.
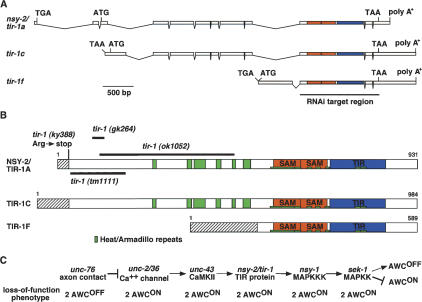
tir-1 encodes a TIR protein. (A) Genomic structure of three variants of F13B10.1 gene. Sequence analysis of cDNA clones corresponding to the F13B10.1 gene revealed six splice forms with alternative 5′ ends, called tir-1a–f. Shown here are tir-1a, tir-1c, and tir-1f, which were identified in this work. tir-1b and tir-1d are similar to tir-1f, and tir-1e is similar to tir-1a and tir-1c (WormBase, http://www.wormbase.org). Boxes and lines represent exons and introns, respectively. ATG and TAA indicate the positions of the putative translational start and stop codons. tir-1a, tir-1c, and tir-1f do not have splice leader sequences at the 5′ end, but have in-frame stop codons preceding the putative translational start codon. The regions that encode SAM and TIR domains are shown in orange and blue, respectively. The region that was targeted by RNAi is underlined. (B) Structure of TIR-1 proteins. Heat/Armadillo repeats, SAM domains, and TIR domain are shown in green, orange, and blue, respectively. Heat/Armadillo repeats are located at amino acids 256–266, 343–354, 360–390, 416–427, 456–464, 484–503, 554–622, 624–634, 649–660, 669–680, 693–703, 774–786, and 789–801 (Mink et al. 2001; Liberati et al. 2004). Hatched boxes indicate isoform-specific regions. (C) Epistasis relationships of nsy mutants. tir-1 may act downstream of unc-43 and upstream of nsy-1.