Figure 2.
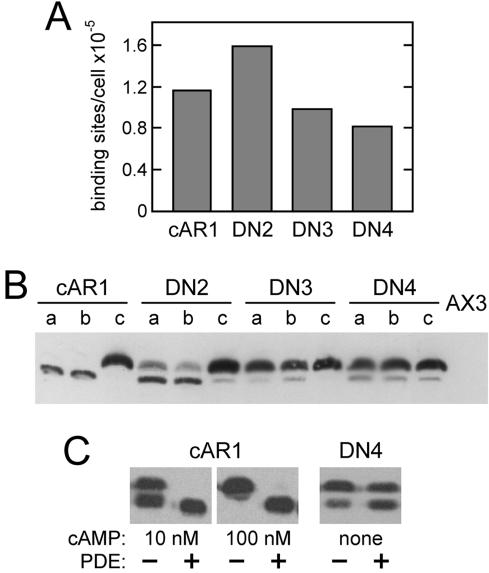
Surface expression and phosphorylation of dominant-negative cAR1 mutants. (A) Receptors on the surface of vegetative cAR1 cells or the indicated DN cells were measured by the binding of 20 nM [3H]cAMP in ammonium sulfate. Wild-type cAR1 is nearly saturated under these conditions. (B) To assess total receptor amounts and phosphorylation, the same cells (2 × 106/ml in PB) were shaken at 22°C for 15 min with no addition (a lanes), 5 mM caffeine (b lanes), or 1 μM cAMP (c lanes). Treated cells were extracted with CHAPS as previously described (Hereld et al., 1994) and cAR1 in the insoluble fraction from 2 × 106 cells was immunoblotted using cAR1 antiserum R4 (gift of P. Devreotes) and chemiluminescent detection. Parental AX3 cells (far right lane) show that little endogenous cAR1 is expressed under these conditions. Comparison of cAR1 lanes b and c indicates that the lower cAR1 band is inefficiently detected in this blot. (C) Effect of phosphodiesterase (PDE) treatment on receptor phosphorylation. Vegetative cAR1 cells (2 × 106/ml in PB) were stimulated with cAMP as indicated for 5 min to induce phosphorylation and were subsequently incubated 15 min without or with PDE. Unstimulated DN4 cells were similarly treated without and with PDE for 20 min. The cells were shaken constantly at 22°C throughout these treatments. Partially purified PDE, included at 3.2 μg protein/ml, was prepared from Dictyostelium as described by van Haastert and van der Heijden (1983). Samples (106 cells each) were CHAPS-extracted on ice and immunoblotted for cAR1 as described above.
