Figure 1.
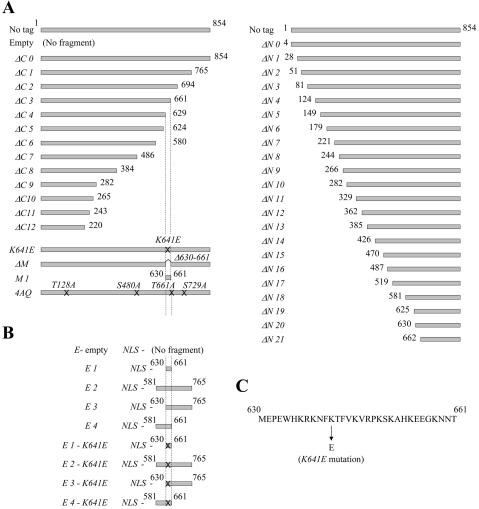
Diagram of the wild-type and the constructed xrs2 mutants. (A) xrs2 mutations analyzed in this study. No tag indicates the wild-type XRS2 gene without an epitope tag sequence. The xrs2-ΔC0 allele is abbreviated to ΔC0; similar abbreviations are used for both the C- and N-terminal xrs2 mutations. Crosses on the gray bars indicate xrs2 alleles containing point mutations created by PCR mutagenesis. All of the xrs2 alleles containing N-terminal truncations encode the first three amino acid residues of Xrs2p, followed by the 3Myc tag at the deletion point. (B) Constructs of Xrs2-E1 to -E4 proteins and their derivatives. All bear a nuclear localization signal (NLS) and the 9Myc tag at their N and C termini, respectively. All of the constructs shown were integrated into the MET17 locus of xrs2 null strains. They also were cloned into the ARS CEN plasmid pRS318 for analysis in the synthetic senescence assay. (C) Amino acid sequence of the MBX.
