Figure 3.
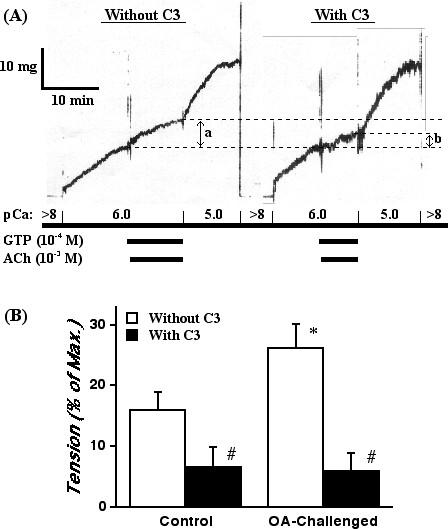
Effect of Clostridium botulinum C3 exoenzyme, an inhibitor of RhoA protein, on the acetylcholine (ACh)-induced Ca2+ sensitization of the α-toxin-permeabilized bronchial smooth muscle of mice. (A) Typical recordings of contraction induced by Ca2+ (pCa 6.0 and 5.0) and ACh (10-3 M) with guanosine triphosphate (GTP; 10-4 M) in α-toxin-permeabilized bronchial smooth muscle isolated from a sensitized control mouse. In the presence of GTP, ACh induced a further contraction even in the constant Ca2+ concentration at pCa 6.0, i.e., ACh-induced Ca2+ sensitization (a). The ACh-induced Ca2+ sensitization was re-estimated after treatment with C3 exoenzyme (10 μg/mL, for 20 min; b). (B) Summary of the effects of C3 exoenzyme on the ACh-induced Ca2+ sensitization of bronchial smooth muscle contraction in the sensitized control (Control) and repeatedly ovalbumin (OA)-challenged (OA-challenged) mice. The data are expressed as percentage increase in tension induced by ACh (in the presence of Ca2+ and GTP) from the sustained contraction induced by pCa 6.0. Each column represents the mean ± S.E. from 6 experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. Control group (Before C3) and #P < 0.05 vs. respective Before C3 group by Bonferroni/Dunn's test.
